Encountering an Excel formula error can be a frustrating and confusing experience.
Messages like #DIV/0!, #NAME?, or #REF! may seem confusing at first, but they follow clear patterns. Understanding these messages is the first step in Excel formula troubleshooting.
In this guide, we will break down each common error, explaining what it means, what causes it, and most importantly, how to fix Excel formula errors.
We’ll also explore how to use the IFERROR function to prevent errors from appearing in the first place and provide valuable tips for future troubleshooting.
How to Use IFERROR to Instantly Handle Excel Errors
Excel’s IFERROR function is a lifesaver for managing errors gracefully. Instead of displaying confusing error codes, IFERROR lets you replace them with custom messages, blank cells, or alternative calculations.
How IFERROR Works
The syntax is simple:
=IFERROR(original_formula, fallback_value)
For example:
- Without IFERROR: =A1/B1 shows #DIV/0! if B1 is zero.
- With IFERROR: =IFERROR(A1/B1, “Check input”) displays “Check input” instead of an error.
When to Use IFERROR
- Expected errors: Use it for benign issues, like missing data in a VLOOKUP:
- =IFERROR(VLOOKUP(D1, A2:B10, 2, FALSE), “Not found”)
- Dashboards/reports: Improve readability by hiding errors with blanks (“ ”) or zeros (0).
Note: IFERROR should not hide unresolved issues. Always check why an error occurs before applying it.
Now that you know how to handle errors proactively, let’s decode what each Excel error code means.
Common Excel Error Codes Explained
When a formula can’t calculate properly, Excel returns an error code instead of a result. Understanding what each one means is the first step to fixing it.
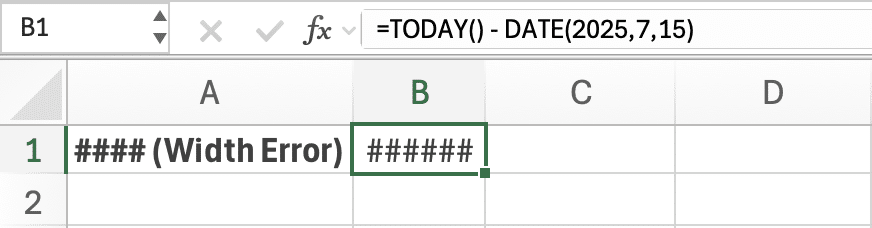
1. #### (Display Error)
Cause: Column width is too narrow to display the content, or a negative date/time exists.
Fix: Widen the column or adjust formatting.
Error Example: =TODAY() – DATE(2025,7,15) displays #### if the column is too narrow.
This is often the easiest error to fix. The following errors, however, require a closer look at your formulas.
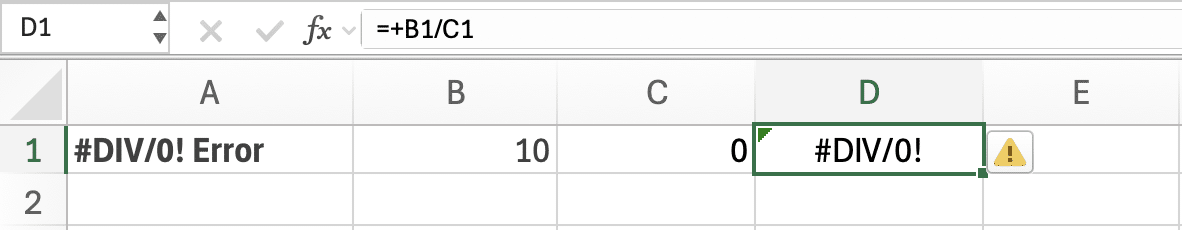
2. #DIV/0! (Division Error)
Cause: Dividing by zero or an empty cell.
Fix:
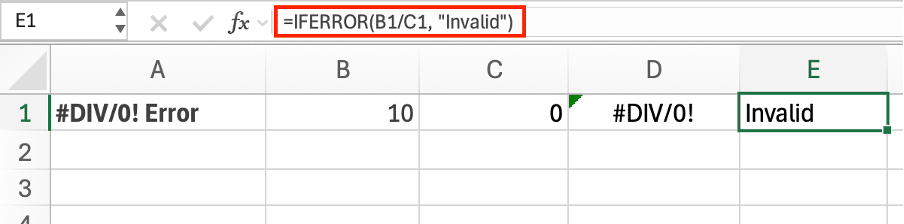
- Use =IFERROR(A1/B1, “”) to show a blank.
- Validate denominators with =IF(B1=0, “Invalid”, A1/B1).
Error Example: =B1/C1 fails if C1 is 0.
Before:
After with IFERROR:
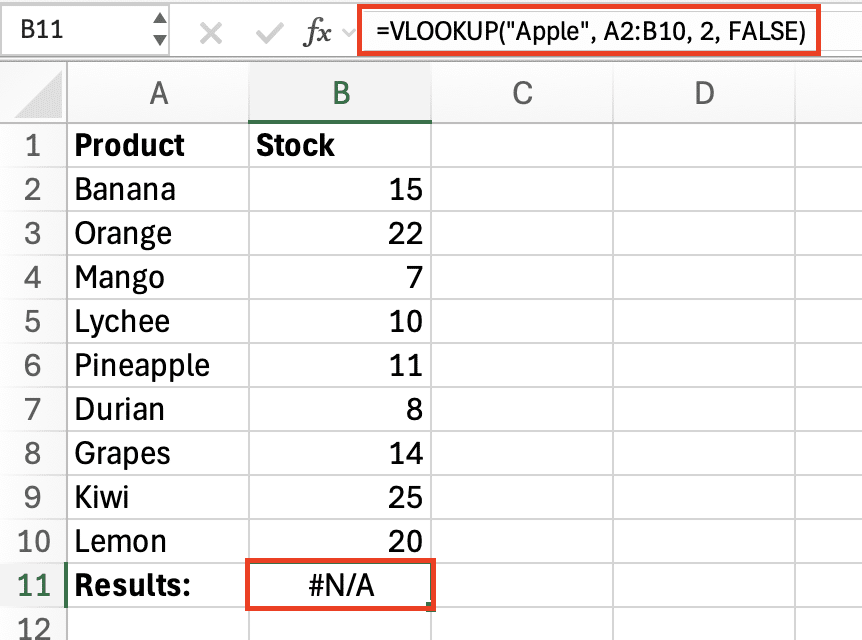
3. #N/A (Lookup Error)
Cause: A lookup function (e.g., VLOOKUP) cannot find a value.
Fix:
- Clean data with =TRIM()
- Verify the lookup range is correct
Error Example: =VLOOKUP(“Apple”, A2:B10, 2, FALSE) returns #N/A if “Apple” is missing.
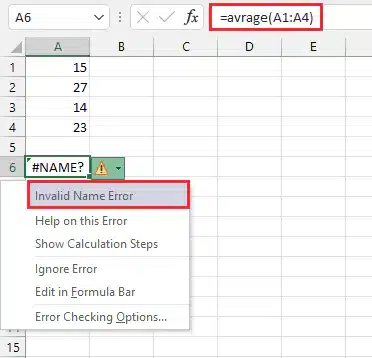
4. #NAME? (Syntax Error)
Cause: A misspelt or non-existent function or range name or unquoted text.
Fix:
- Correct spelling (e.g., =SUM instead of =SUm).
- Enclose text in quotes: =IF(A1=”Yes”, 1, 0)
Error Example:
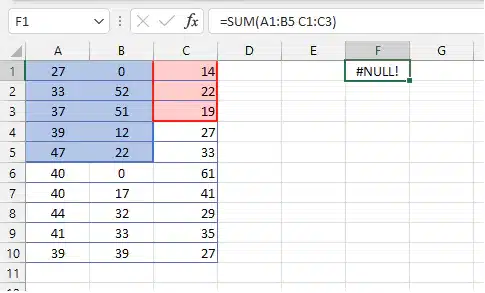
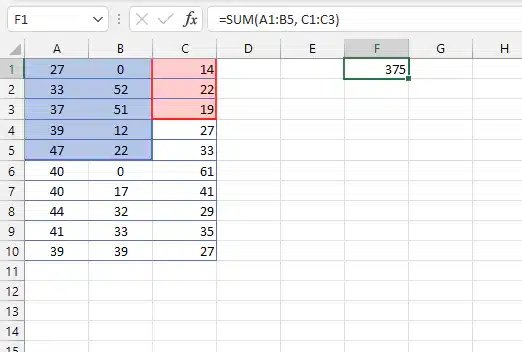
5. #NULL! (Range Error)
Cause: Incorrect use of range operators (space instead of colon or comma).
Fix: Replace spaces =SUM(A1:A10) or =SUM(A1,A10).
Error Example (Without comma):
After Fix (After adding comma):
After reviewing your formula’s structure, it’s also important to check if the numbers themselves can be calculated.
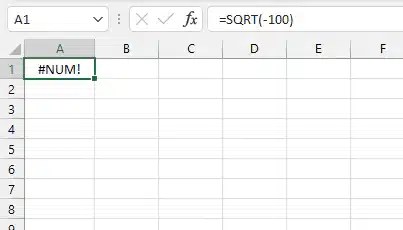
6. #NUM! (Calculation Error)
Cause: Invalid math operations (e.g., =SQRT(-100)).
Fix: Ensure inputs are valid or adjust formulas.
Error Example:
7. #REF! (Reference Error)
Cause: A cell or sheet reference is broken (e.g., after deletion).
Fix: Restore deleted data or update the formula.
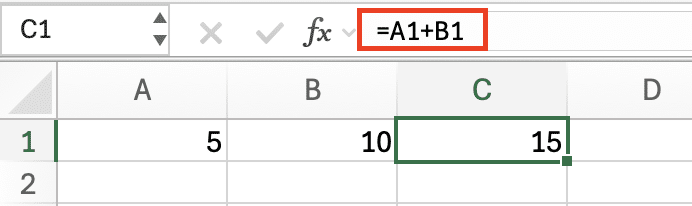
Example: =A1+B1 becomes =A1+#REF! if column B is deleted.
Before Deletion:
After Deleting Column B:
Reference errors occur when cells are moved or deleted. A more modern error, #SPILL!, happens when new array functions don’t have room to display results.
8. #SPILL! (Array Error)
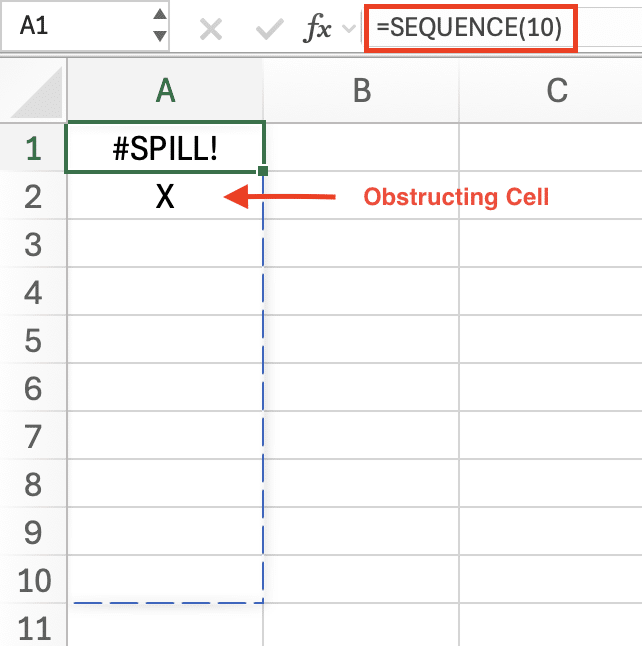
Cause: A dynamic array formula (e.g., =SEQUENCE(10)) is blocked by existing data.
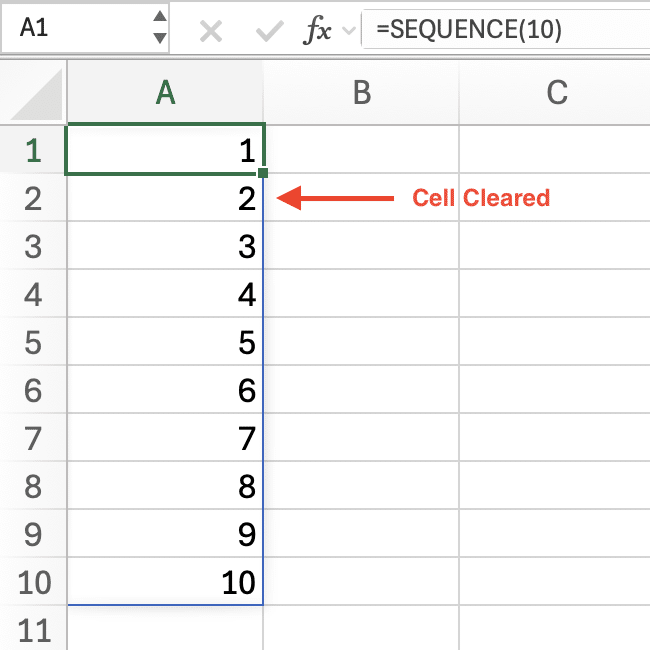
Fix: Clear the obstructing cells or move the formula.
Error Example:
After Fix:
The #SPILL! error is unique to dynamic arrays, while the #VALUE! error is one of the most common and generic errors.
9. #VALUE! (Data Type Error)
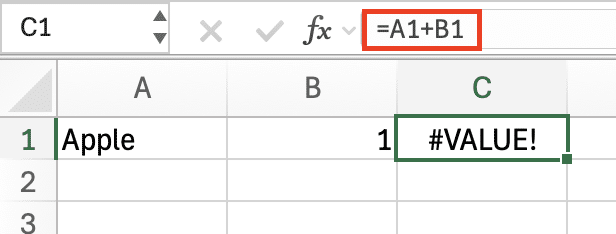
Cause: Mixing incompatible data types (e.g., text with numbers).
Fix: Use =VALUE() or ensure consistent data types.
Error Example: =”Apple”=1 returns #VALUE! because text cannot be added to a number.
Now that you can identify and fix these common errors, you can take proactive steps to prevent them from appearing in the first place.
Best Practices to Avoid Excel Errors
Prevention is always better than correction. Adopting a few careful habits can drastically reduce the number of errors you encounter in your work.
- Clean imported data with =TRIM() and =CLEAN() to remove extra spaces or non-printable characters.
- Store fixed values separately (e.g., tax rates in a dedicated cell) instead of hardcoding them in formulas.
- Use absolute references ($A$1) when copying formulas to prevent incorrect references.
- Check for errors early using Excel’s built-in tools:
- Error Checking: Highlights potential issues.
- Trace Precedents: Shows which cells a formula depends on.
- Avoid masking errors with IFERROR unless you understand and accept the cause.
By understanding these errors and implementing the prevention strategies above, you are well on your way to creating more robust and reliable spreadsheets.
Let’s recap the key takeaways.
Conclusion
Excel errors are common; they can also be resolved quickly once you know what to look for.
By understanding the meaning behind each error code and applying the right fixes, such as IFERROR for controlled fallbacks or =TRIM() for clean data, you can minimise disruptions and work more efficiently.
Bookmark this handy guide for future troubleshooting!
Ready to Move from Fixing Errors to Mastering Excel?
Understanding errors is just the first step. Imagine building spreadsheets that are powerful, efficient, and error-proof from the start.
Explore Microsoft Excel Courses designed for professionals at every level, turning confusion into confidence and tasks into breakthroughs.
Find your perfect fit:
- WSQ Microsoft Excel Essentials: Learn the basics of Excel, from formulas to formatting, for efficient spreadsheet use.
- WSQ Microsoft Excel Intermediate: Build on your skills with advanced functions and data analysis tools.
- WSQ Microsoft Excel Advanced: Learn to use Excel’s advanced features for data-driven decision making and reporting.
Stop struggling and start excelling! Enrol with us today!
Related Courses
- Data Analysis with Microsoft Excel DASHBOARD Reporting for Management
- WSQ Data Visualisation and Storytelling with Power BI
- WSQ Data Visualisation and Storytelling with Tableau
◆◆◆