Today, navigating the demands of the world requires more. technical skills are important, but they represent only part of the equation. Emotional intelligence (EQ), encompassing skills beyond traditional IQ, is now increasingly recognised as essential for navigating both personal and professional success. Research indicates that a remarkable 58% of overall job success is attributed to emotional intelligence (EQ), highlighting its significance across various roles.
This is especially true in leadership, where EQ is increasingly recognised as essential for connecting with teams and navigating complex emotional landscapes. Whether you’re aiming for career advancement, building strong relationships, or just navigating everyday life, our EQ makes a huge difference.
This article is your guide to understanding what EQ is all about, why it matters, and how you can develop it for personal and professional growth.
With that in mind, let’s explore the core components that make up emotional intelligence.
What is Emotional Intelligence?
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is the ability to understand and manage your emotions while also recognising and influencing the emotions of others. It’s a skill that helps you navigate relationships, make thoughtful decisions, and handle challenges effectively whether at work, at home, or in everyday life. Dr. Daniel Goleman, a leading expert on emotional intelligence breaks it down into four key areas:
#1 Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is the ability to notice and understand your emotions as they happen. When you’re in tune with your feelings, you can see how they influence your thoughts and behaviours, making it easier to respond thoughtfully instead of reacting impulsively.
Example: You realise you’re feeling frustrated after a long day. Instead of taking it out on a friend or colleague, you acknowledge the emotion and take a moment to reset. Self-awareness is like having an internal compass, it helps you stay in control, even when emotions run high.
#2 Self-Management
Once you’re aware of your emotions, the next step is learning how to manage them effectively. Self-management is about staying composed, adaptable, and proactive rather than reactive. It helps you think before you act and maintain a sense of balance, even in high-pressure situations.
Example: You receive unexpected criticism at work. Instead of getting defensive, you pause, take a deep breath, and consider the feedback with an open mind. Self-management doesn’t mean ignoring emotions. It means channelling them in a way that works for you, not against you.
#3 Social Awareness
Have you ever had a conversation where someone just “gets” you? That’s social awareness in action. It’s the ability to tune in to other people’s emotions, read the room, and understand different perspectives.
Example: You notice a colleague is quieter than usual during a meeting. Instead of assuming they’re uninterested, you check in with them privately to see if they need support. Being socially aware helps you connect more deeply with others, whether you’re leading a team, working with clients, or simply strengthening your relationships.
#4 Relationship Management
Whether you’re resolving a conflict, leading a project, or simply having a conversation, relationship management is what keeps things running smoothly. It’s about communicating clearly, handling disagreements with maturity, and fostering positive connections.
Example: A disagreement comes up in a group discussion. Instead of letting it escalate, you keep the conversation constructive and help find common ground. Good relationship management isn’t about avoiding conflict—it’s about handling it with confidence and respect. 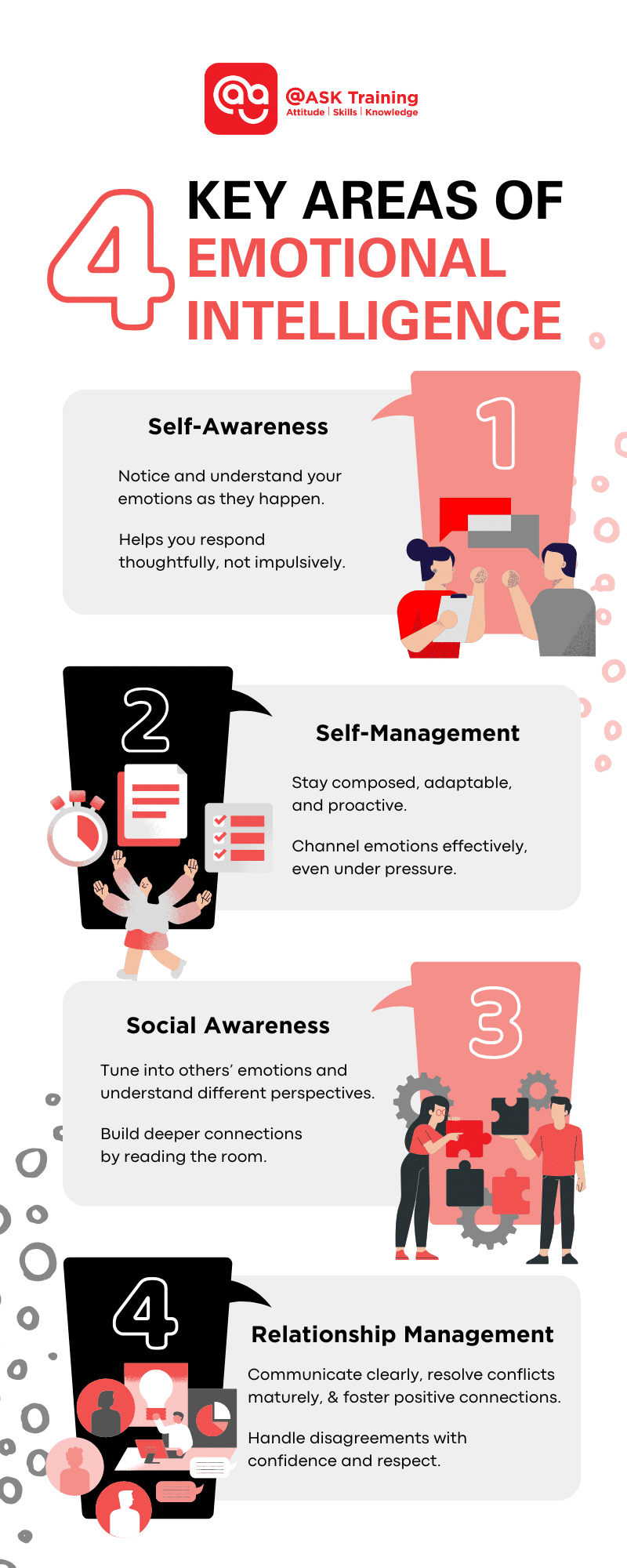
Let’s explore the tangible benefits it offers for your personal and professional life.
Benefits of Emotional Intelligence
Cultivating emotional intelligence isn’t just a feel-good exercise; it has a profound impact on various aspects of your life, both personally and professionally. Here are some key advantages:
Improved Communication and Conflict Resolution
EQ enhances your ability to communicate clearly and effectively. You become a better listener, more attuned to nonverbal cues, and more capable of expressing your own thoughts and feelings constructively.
This leads to fewer misunderstandings and smoother interactions. When conflicts do arise (as they inevitably will), your EQ skills help you navigate disagreements with empathy and find mutually beneficial solutions. You’re less likely to react impulsively and more likely to approach conflict with a calm and reasoned approach.
Example: In a team meeting, you notice a colleague seems hesitant to share their ideas, so you create a safe space for them to speak up, leading to a valuable contribution to the project.
Enhanced Decision-Making
Emotions often play a significant role in our decision-making processes. With higher EQ, you become more aware of how your emotions are influencing your choices. This awareness allows you to make more rational and balanced decisions, especially in stressful or high-pressure situations.
You’re less likely to make impulsive decisions based on fleeting emotions and more likely to consider the long-term consequences of your actions.
Example: When faced with a tight deadline and mounting pressure, you take a step back to assess the situation objectively rather than making a hasty decision driven by anxiety.
Stronger and More Fulfilling Relationships
EQ is the cornerstone of healthy relationships. By developing empathy and social skills, you build stronger connections with others. You’re better able to understand their perspectives, offer support, and build trust.
This translates to more fulfilling relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. You’re better equipped to handle disagreements constructively and maintain positive connections even during challenging times.
Example: You offer a listening ear and words of encouragement to a friend going through a difficult breakup, demonstrating empathy and strengthening your bond.
Increased Resilience and Stress Management
Life throws curveballs, and how you handle them matters. EQ helps you manage stress more effectively by providing you with the tools to regulate your emotions and bounce back from setbacks.
You develop a more positive outlook, become more adaptable to change, and handle pressure with greater ease. This resilience not only improves your well-being but also enhances your ability to perform under pressure.
Example: After receiving constructive criticism on a project, you acknowledge the feedback, learn from it, and use it to improve your future work, rather than becoming discouraged.
Greater Leadership Effectiveness and Workplace Success
In the workplace, EQ is a game-changer. Leaders with high EQ inspire and motivate their teams, build strong working relationships, and foster a positive and productive work environment.
They are better at understanding team dynamics, resolving conflicts, and communicating a clear vision. This translates to increased team morale, higher productivity, and greater overall success.
EQ is not just beneficial for leaders; it’s valuable for everyone in the workplace, contributing to better teamwork, communication, and overall workplace harmony.
Example: A manager with high EQ recognises when their team is feeling overwhelmed and adjusts workloads or provides additional support. They also celebrate team successes and acknowledge individual contributions, boosting morale. Now that we’ve explored the benefits of emotional intelligence, let’s take a look at how EQ plays out in everyday situations, both at home and at work.
How Emotional Intelligence Impacts Daily Life
We’ve seen the impressive benefits of developing EQ, but how does it actually manifest in our daily lives? Let’s go through some practical examples of how EQ impacts both personal and professional settings.
EQ in Personal Life
Managing Emotions
Imagine you’ve had a stressful day at work. Instead of taking your frustration out on your family, you recognise your heightened emotional state (self-awareness) and choose to take a few minutes to de-stress before interacting with them (self-regulation). This simple act of emotional management prevents potential conflict and maintains a positive home environment.
Another example is when you experience a setback, like not getting the promotion you were hoping for. Instead of dwelling on disappointment, you acknowledge the feeling and then shift your focus to identifying what you can learn from the experience and how you can improve in the future (motivation).
Building Empathy
A friend confides in you about a personal struggle they’re facing. Instead of offering unsolicited advice, you listen attentively, try to understand their perspective, and offer genuine empathy and support. This strengthens your bond and creates a safe space for open communication.
Another example is when you try to understand the opposing viewpoints during a family disagreement. Instead of getting defensive, you try to put yourself in their shoes and understand their perspective, leading to a calmer and more productive conversation.
Improving Relationships
EQ plays a crucial role in building and maintaining healthy relationships. For instance, during a disagreement with your partner, you use active listening to understand their concerns and express your own feelings respectfully. This prevents escalation and fosters a stronger connection.
Another example is when you proactively express appreciation and gratitude to loved ones, strengthening bonds and fostering a positive atmosphere.
EQ in Professional Life
Teamwork
In a team project, you notice that one team member is struggling to keep up. Instead of criticising them, you offer support and guidance, demonstrating empathy and strengthening team cohesion.
You also actively listen to everyone’s ideas and facilitate open communication, ensuring everyone feels heard and valued. This leads to better collaboration and a more successful project outcome.
Leadership
As a leader, you recognise when your team is feeling stressed due to an upcoming deadline. You address their concerns, offer support, and adjust workloads if necessary.
This demonstrates empathy and builds trust, leading to increased team morale and productivity. You also provide constructive feedback in a way that is motivating and encouraging, fostering growth and development within the team.
Career Advancement
EQ is a crucial factor in career progression. For example, during a job interview, you demonstrate strong communication skills, confidence, and the ability to connect with the interviewer on a personal level.
This creates a positive impression and increases your chances of landing the job. Another example is when you handle workplace conflicts with professionalism and diplomacy, demonstrating strong social skills and building positive relationships with colleagues and superiors, which can open doors to new opportunities.
Real-World Scenarios Showcasing the Power of EQ
Scenario 1: Customer Service
A customer calls with a complaint about a faulty product. A customer service representative with high EQ listens empathetically to the customer’s frustration, acknowledges their feelings, and takes ownership of the problem.
They then offer a solution that satisfies the customer, turning a potentially negative experience into a positive one and building customer loyalty.
Scenario 2: Project Management
A project manager with high EQ notices that their team is experiencing burnout due to long hours and tight deadlines. They proactively address the issue by adjusting the project timeline, providing additional resources, and offering words of encouragement.
This boosts team morale, reduces stress, and ultimately leads to a successful project completion.
Scenario 3: Negotiation
Two business partners are in disagreement about the terms of a new contract. A skilled negotiator with high EQ listens carefully to both sides, understands their underlying needs and concerns, and finds a compromise that satisfies both parties.
This preserves the business relationship and leads to a mutually beneficial outcome. From these examples, you would have an idea of how EQ isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s a practical skill that significantly impacts our interactions, relationships, and overall success in both personal and professional life.
Now, let’s explore how you can actively develop your own emotional intelligence.
How to Develop Emotional Intelligence
We’ve seen how EQ impacts our lives, so let’s focus on the practical steps you can take to develop and strengthen your own emotional intelligence. Developing EQ is a journey of self-discovery and continuous improvement. These strategies can help you along the way on how to improve EQ:
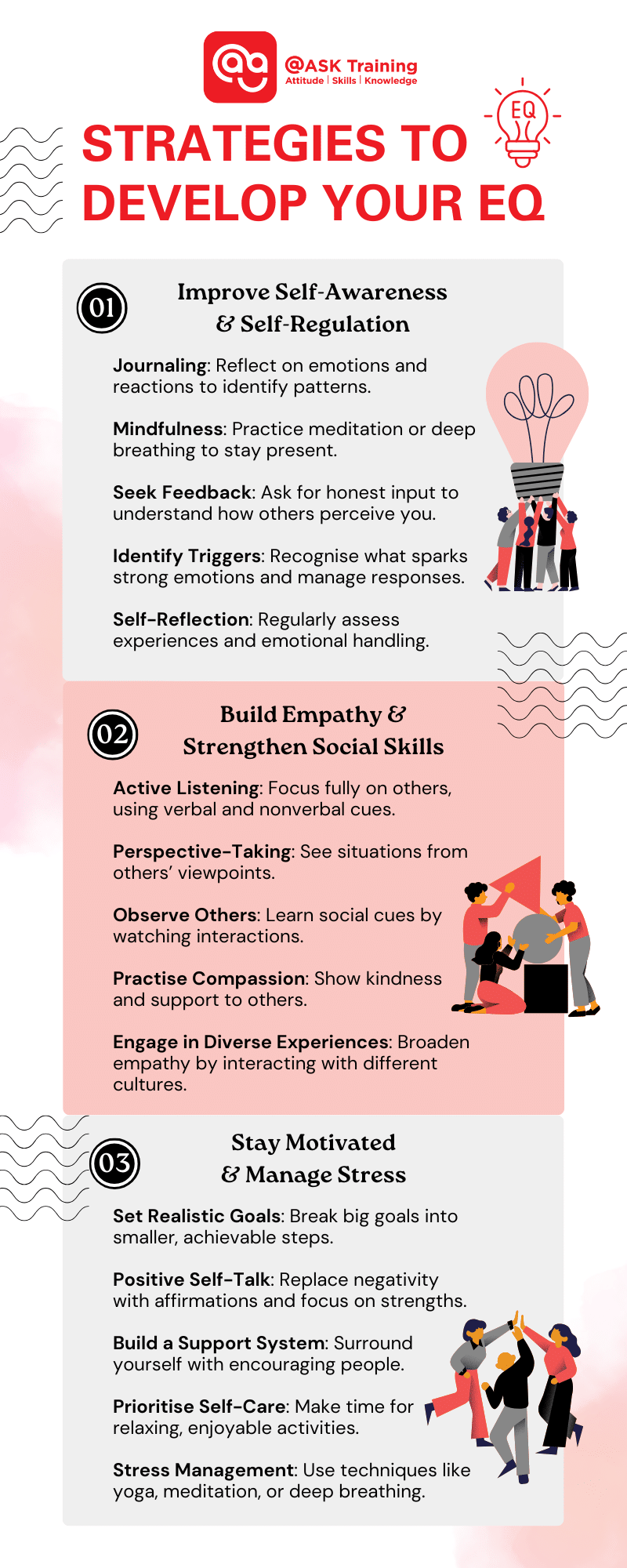
Improving Self-Awareness and Self-Regulation
Journaling
Regularly writing down your thoughts and feelings can be a powerful tool for self-discovery. Reflect on specific situations, how you felt, and why you reacted the way you did. This helps you identify patterns in your emotions and understand your triggers.
In one study, college students who engaged in journaling demonstrated higher EQ scores, suggesting its effectiveness in improving emotional regulation and coping skills. This shows that consistent expressive writing can significantly enhance emotional intelligence.
Mindfulness
Practising mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. Techniques like meditation or deep breathing can help you become more attuned to your bodily sensations and emotional states.
This increased awareness allows you to recognise emotions as they arise rather than being swept away by them.
For example, studies have shown that Transcendental Meditation (TM) can significantly boost your EQ while simultaneously reducing stress levels in the workplace.
Seeking Feedback
Asking trusted friends, family members, or colleagues for honest feedback about your behaviour and interactions can provide valuable insights into how you come across to others.
Be open to constructive criticism and use it as an opportunity for growth.
Identifying Emotional Triggers
Pay attention to the situations, people, or thoughts that tend to trigger strong emotional reactions in you.
Once you identify these triggers, you can develop strategies for managing your responses more effectively.
Practising Self-Reflection
Regularly take time to reflect on your experiences and how you handled them emotionally.
Ask yourself what you could have done differently and what you learned from the situation.
Strategies to Build Empathy and Strengthen Social Skills
Active Listening
This involves fully concentrating on what the other person is saying, both verbally and nonverbally. Pay attention to their body language, tone of voice, and facial expressions. Ask clarifying questions and summarise what you’ve heard to ensure you understand their perspective.
Studies have shown that individuals who receive active listening responses feel more understood than those who receive advice or simple acknowledgements. This demonstrates the power of truly listening and making others feel heard.
Perspective-Taking
Consciously try to put yourself in the other person’s shoes and see things from their point of view. This helps you understand their feelings and motivations, even if you don’t necessarily agree with them.
Observing Others
Pay attention to how people interact with each other in social situations. Observe their communication styles, body language, and emotional responses.
This can help you learn valuable social cues and improve your own interactions.
Practising Compassion
Cultivate a genuine desire to understand and help others. Offer support and encouragement to those who are struggling and show kindness and understanding in your interactions.
Studies have shown that cultivating compassion provides numerous benefits, including increased well-being and reduced stress.
Engaging in Diverse Experiences
Interacting with people from different backgrounds and cultures can broaden your perspective and enhance your empathy. Seek out opportunities to learn about different viewpoints and ways of life.
Techniques for Staying Motivated and Managing Stress
Setting Realistic Goals
Break down large goals into smaller, more manageable steps. This makes them less overwhelming and increases your sense of accomplishment as you make progress.
Practising Positive Self-Talk
Replace negative thoughts with positive affirmations. Focus on your strengths and accomplishments and believe in your ability to overcome challenges.
Developing a Support System
Surround yourself with positive and supportive people who encourage you and lift you up. Having a strong support network can help you stay motivated and manage stress more effectively.
Prioritising Self-Care
Make time for activities that you enjoy and that help you relax and recharge. This could include exercise, spending time in nature, pursuing hobbies, or simply taking time for yourself.
Stress Management Techniques
Learn and practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. These can help you regulate your emotions and manage stress in healthy ways.
EQ Exercises You Can Try
Instead of just telling you about these skills and strategies, let’s give you some concrete ways to start practising them right now!
Here are some engaging exercises you can try:
Journaling: Your Emotional Check-In
Writing down your thoughts and feelings is powerful for self-discovery. Try these prompts:
- Emotional Inventory: At day’s end, list 3 emotions you felt and what triggered them. What did you learn?
- Challenging Your Thoughts: When feeling negative, write down your automatic thoughts. Are they realistic? How can you reframe them positively?
- Gratitude Journal: Regularly list things you’re grateful for to boost your mood and well-being.
- Reflecting on Interactions: After a key interaction, reflect on how you and the other person felt, and how effective your communication was.
For more journaling prompts, try these journal writing resources.
Mindfulness: Finding Your Center
Mindfulness means being present. Even a few minutes daily helps. Try this:
- Body Scan: Lie or sit comfortably and focus on different body parts, noticing sensations without judgment.
- Breath Awareness: Focus on your breath. When your mind wanders, gently return to your breath.
For more mindfulness exercises, you can consider exploring apps like Headspace or Calm which provide guided meditations and mindfulness practises.
Active Listening
Active listening is more than just hearing words; it’s about truly understanding the other person’s perspective.
Try these exercises with a friend or family member:
- Mirroring: After the other person speaks, briefly summarise what you heard in your own words. This shows that you’re paying attention and helps clarify understanding.
- Open-Ended Questions: Ask questions that encourage the other person to elaborate and share more about their thoughts and feelings. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no.”
- Nonverbal Communication: Pay attention to the other person’s body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. These nonverbal cues can provide valuable insights into their emotional state.
Let’s dive in further on how EQ plays a crucial role in the workplace.
Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace
Beyond personal life, EQ plays a vital role in the professional world. EQ impacts everything from individual performance to overall organisational effectiveness. Here’s a deeper look:
The Role of EQ in Leadership and Team Dynamics
High EQ leaders possess key traits that directly translate to improved team performance and a positive work environment:
Empathy
- They understand their team’s feelings, building trust and a supportive environment.
- Example: A leader recognising a team member’s personal struggles and offers flexibility.
Communication
- They communicate clearly and respectfully, ensuring everyone feels heard.
- Example: A leader actively listens to team feedback during a meeting.
Conflict Resolution
- They effectively manage disagreements, finding win-win solutions.
- Example: A leader mediating a conflict between two team members by facilitating open communication.
Motivation
- They inspire teams by recognising strengths and providing constructive feedback.
- Example: A leader celebrating team successes and acknowledging individual contributions.
Self-Awareness
- They understand their impact on others, leading with authenticity.
- Example: A leader acknowledging their own mistake and taking responsibility.
These traits foster positive team dynamics:
- Increased Trust & Collaboration: Open communication and mutual respect drive teamwork.
- Reduced Conflict: Proactive management prevents disruptions.
- Higher Morale & Engagement: Supportive environments lead to happier, more productive teams.
Building A Thriving Workplace with EQ
A workplace with a high level of EQ creates a thriving environment characterised by:
- Reduced Stress and Burnout: When employees feel supported and understood, they experience less stress and are less likely to burn out.
- Increased Job Satisfaction: Employees who feel valued and respected are more satisfied with their jobs and more likely to stay with the company.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Open communication and effective collaboration lead to smoother workflows and better problem-solving.
- Enhanced Innovation and Creativity: A positive and supportive environment encourages employees to take risks and share new ideas.
- Increased Productivity and Performance: When employees are engaged, motivated, and supported, they are more productive and achieve better results.
Theory is important, but seeing EQ in action is even more inspiring.
Let’s take a look at some real-world examples of leaders who have demonstrated exceptional EQ.
Real-World Examples from Real-World Leaders
While it’s difficult to definitively quantify EQ in historical figures, many successful leaders throughout history have demonstrated strong emotional intelligence through their actions and leadership styles. Here are some notable examples:
Tim Cook (CEO, Apple)
(Source: Apple Insider)
When Tim Cook stepped into Steve Jobs’ shoes as Apple’s CEO, he faced an enormous challenge. Jobs was known for his visionary leadership and strong personality, and many wondered whether Cook could fill that role. Instead of trying to mimic his predecessor, Cook leaned into his own strengths—empathy, humility, and emotional intelligence to lead Apple into a new era of success.
Unlike Jobs’ high-intensity, perfectionist approach, Cook cultivated a leadership style centered around listening, collaboration, and trust. He recognised that great leadership isn’t about having all the answers, it’s about empowering others.
Indra Nooyi (Former CEO of PepsiCo)
(Source: Leadership Matters)
Nooyi was known for her empathetic leadership style and her focus on building strong, personal relationships with employees at all levels of the organisation. She prioritised open communication, fostered a culture of inclusivity and respect, and championed initiatives that benefited both the company and its employees.
Her focus on “Performance with Purpose” also demonstrates an understanding of the broader impact of business and the importance of social responsibility.
Satya Nadella (CEO, Microsoft)
(Source: The New York Times)
Satya Nadella took over Microsoft at a time when the company’s culture was rigid and competitive. Recognising the need for change, he shifted the mindset from “know-it-all” to “learn-it-all,” fostering a culture of growth, innovation, and inclusion. His leadership is rooted in self-awareness and social awareness, ensuring employees feel valued while driving Microsoft’s transformation into a cloud-first, AI-driven company.
By embracing empathy and collaboration, Nadella broke down silos, encouraged learning, and positioned Microsoft for long-term success.
These leaders prove that EQ isn’t just a “soft skill”—it’s a critical driver of success in leadership, team dynamics, and creating thriving workplace environments.
Wrapping Up
Ultimately, emotional intelligence (EQ) is an investment in your future. By developing these skills, you’re not only improving your current relationships and performance but also laying the foundation for long-term success and fulfilment.
Whether you’re aiming for career advancement, stronger personal connections, or simply greater well-being, EQ can help you achieve your goals.
We encourage you to start practising the techniques we’ve discussed. You’ll be surprised at the positive impact even small changes can have!
Ready to Take Your EQ Journey Further?
If you’re looking to translate these insights into practical skills, @ASK Training offers a variety of Leadership and Management courses!
Our Mastering Emotional Intelligence: Your Key to People Management Excellence! provides practical tools and strategies to deepen your emotional intelligence skills.
Get in touch with us today to learn more!









