You’ve probably heard the term in the news: quantum computing. It sounds like science fiction, but it’s a very real technology that’s advancing quickly. So, what is it, and why does it matter?
In simple terms, it’s a completely new way of building computers that uses the rules of quantum physics.
This guide will break down what is quantum computing in plain English, without the complex jargon. We’ll explore how it works, why it’s such a big deal, and how you can start to understand this exciting field.
What is a Quantum Computer?
To understand quantum computing, first recognise how your current computer works. Classical computers process information step-by-step, like following a recipe.
They’re efficient for everyday tasks but hit a wall with problems that have millions of possible solutions.
Quantum Computer Explained Simply
A quantum computer takes a completely different approach. Instead of checking one solution at a time, it can explore countless possibilities simultaneously. But here’s the critical detail most people miss:
A quantum computer doesn’t work alone.
Think of it as a specialised co-processor, an expert that tackles only the most complex, parallel part of a problem.
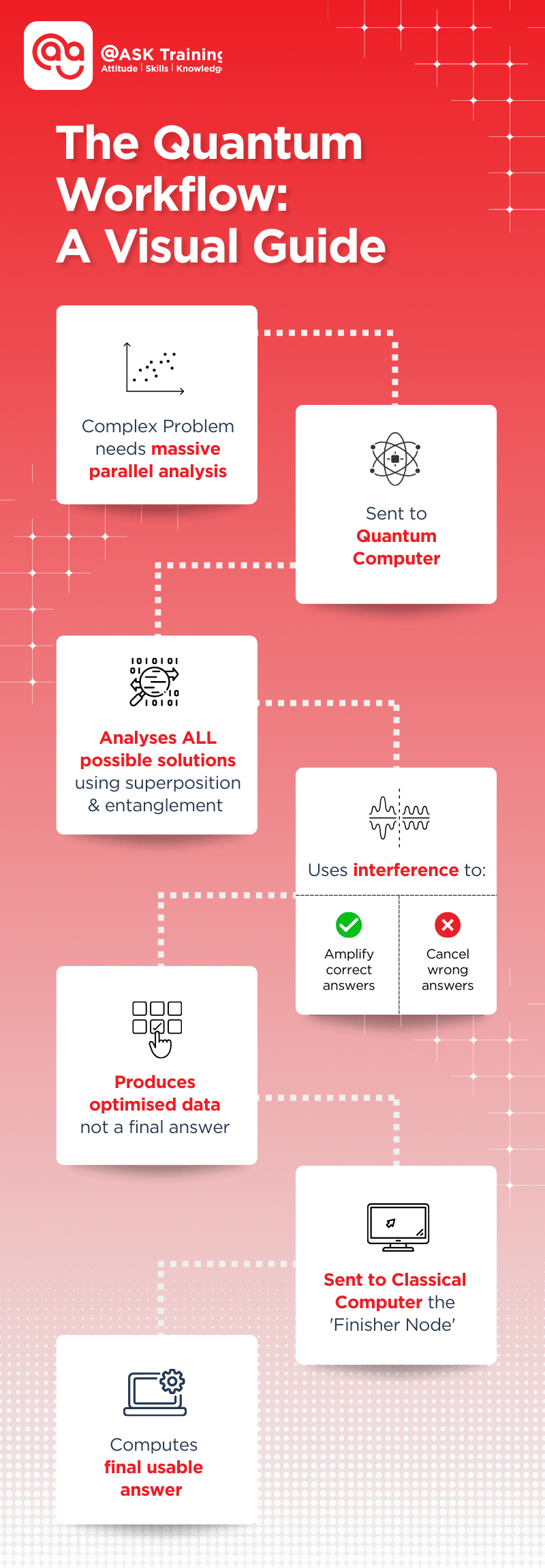
It analyses all possible solutions at once, filters out the wrong ones, amplifies the right patterns, and then hands the optimised data to a classical “finisher” computer to produce the final, usable answer.
The Quantum Workflow: A Visual Guide
Here’s exactly how the hybrid process works, step-by-step:
Simple analogy: Finding the fastest delivery route across Singapore with 100 stops.
- A normal computer checks routes one by one (could take years to calculate).
- A quantum computer evaluates all route combinations simultaneously → finds the optimal pattern → sends it to a classical computer to map the final route.
From Bits to Qubits: The Core Difference
The differences start at the most basic level: how information is stored and processed. This is the essential qubits vs bits discussion.
Classical Bits (What We Use Now):
- Like a light switch: either ON (1) or OFF (0)
- Every email, photo, and app is just long strings of 0s and 1s
- Processes information in sequence, one step at a time
Quantum Qubits(The Quantum Advantage)
- Can be 0, 1, or any combination of both at the same time
- Think of a spinning coin; while it spins, it’s not just heads or tails, but a blur of both possibilities
- This allows quantum computing to process massive amounts of data in parallel
Important note: Qubits are extremely delicate. This sensitivity is one of the biggest challenges in advancing quantum technology.
Key Quantum Principles
You might be wondering, how can something be two things at once? It helps to understand the three strange rules that make it possible.
Let’s look at the core principles that make quantum computing tick.
Superposition
- This is the qubit’s ability to exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- It’s why a quantum computer can load and analyse millions of possibilities at once, rather than sequentially.
Entanglement
- When qubits become entangled, they form a deep connection.
- Change one, and the other instantly changes too—no matter how far apart they are.
- This allows qubits to work together as a deeply interconnected system.
Interference
- This is how quantum computers get useful results from all that parallel processing.
- Quantum algorithms are designed to make the probability waves representing correct answers reinforce each other, while waves representing wrong answers cancel each other out.
- Essentially, it filters noise and highlights the best solutions.
Why Quantum Computing Matters?
The potential of this technology isn’t just theoretical; it’s poised to tackle concrete challenges across various sectors.
The most promising quantum computing applications lie in solving optimisation, simulation, and machine learning problems that are currently intractable.
Consider these potential use cases:
In Finance:
- Optimising investment portfolios with millions of variables
- Performing real-time risk analysis for global markets
- Enhancing fraud detection through complex pattern recognition
In Logistics & Supply Chain:
- Finding optimal global shipping and air traffic routes
- Coordinating warehouse robotics for maximum efficiency
- Managing complex supply chain networks in real-time
In Healthcare & Materials Science:
- Accelerating drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions
- Designing new materials for better batteries and electronics
- Modelling complex chemical reactions for clean energy solutions
In Cybersecurity:
- The challenge: Quantum computers could potentially break current encryption methods.
- The opportunity: They also enable the development of quantum-safe encryption to future-proof our digital infrastructure.
Given this vast potential, it’s clear why there’s a global race to advance this technology. But where are we in that race today?
Current Challenges and Limitations
While headlines might make it seem like quantum supremacy is just around the corner, the reality is that the field remains in its early, experimental stages. A tone of cautious optimism is definitely warranted.
Researchers are currently tackling several significant challenges:
Qubit Stability
Qubits are incredibly delicate. The main challenge is maintaining their quantum state long enough to complete meaningful calculations before they lose their special properties—a problem known as “decoherence.”
Error Correction
Qubits are prone to errors. Correcting these mistakes requires complex techniques that need many physical qubits just to create one stable, reliable “logical qubit.”
Scalability
We can currently build machines with a few hundred qubits, but constructing systems with the thousands or millions of high-quality, interconnected qubits needed for groundbreaking applications is a massive engineering challenge.
Global research is intensely focused on overcoming these barriers. Progress is steady, but creating large-scale, reliable quantum computers is a long-term goal, likely still a decade or more away.
This global context raises an important question for us locally: what is Singapore’s role in this exciting technological frontier?
Quantum Computing in Singapore: A Strategic National Priority
Singapore has no intention of being a spectator in the quantum revolution. Recognising the strategic importance of this technology, the government has committed significant resources, including a S$300 million National Quantum Strategy (NQS), to build a world-class ecosystem.
This commitment is already visible through key initiatives:
Research Hubs:
The Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT) at NUS is a globally recognised research centre, while the National Quantum Computing Hub (NQCH) focuses on developing and providing access to quantum hardware.
Industry Collaboration:
Entities such as A*STAR’s IHPC are driving applied research, while companies like OCBC are exploring quantum computing applications in finance.
Projects like the National Quantum-Safe Network Plus (NQSN+) are preparing the country’s infrastructure for future threats.
Singapore’sStrategy is Holistic:
Leveraging its strong R&D base, fostering public-private partnerships, and developing homegrown talent to secure its position as a quantum node in Asia.
With a national strategy in place, many professionals and students are wondering how they can be part of this emerging field.
Should You Learn About Quantum Computing?
For professionals and students in Singapore, the rise of quantum technology presents a unique opportunity. The question isn’t “Do I need a PhD to contribute?” but rather, “How can I build foundational knowledge to stay relevant?“
The pathway is more accessible than you might think:
Start with the Basics
A strong foundation in linear algebra, probability, and Python programming is highly valuable. A deep physics background is not a prerequisite to start learning.
Leverage Local and Online Resources
Explore workshops from the NQCH, university short courses, and the excellent (and free) online learning tools provided by IBM Quantum and its Qiskit platform.
Think in Terms of Layers
You don’t need to build a quantum computer to use one. Future roles will span hardware, software development, algorithm design, and industry-specific application experts.
Learning now is not about mastering the technology overnight. It’s about building quantum literacy, understanding its potential and limitations, to position yourself at the forefront of the future of computing in Singapore.
Wrapping Up: Your Quantum Journey
Quantum computing is a fascinating and complex field, but its core ideas can be understood by anyone. It represents a fundamental shift from traditional computing, harnessing the unique properties of quantum mechanics to solve problems in powerful new ways.
The journey from lab to our daily lives is still underway, but the progress is undeniable. We hope this guide has explained what is quantum computing and sparked your interest.
Remember, every expert was once a beginner. Why not take the first step in your quantum computing journey today?
Future-Proof Your Tech Career!
Explore @ASK Training’s curated list of introductory guides to other emerging technologies like AI and cybersecurity to build a comprehensive understanding of the digital landscape.
If you’re looking to boost your skills and future-proof your career, consider exploring one of our popular foundational courses:
- Emerging Technologies and Trends: Get a comprehensive overview of the technologies shaping our future, from AI to Green Computing and beyond.
- Introduction to IT: Build a robust understanding of the fundamental concepts that power the digital world.
- Cybersecurity Essentials: Learn how to protect data and systems in an increasingly connected and vulnerable landscape.
Enrol with us today and build a stronger tech foundation!
Related Courses
- Certificate in Infocomm Technology (Infrastructure and Operations)
- IT Foundations Courses
- Cloud Computing
- Cybersecurity Courses
◆◆◆