Cybersecurity is essential in today’s digital age to protect sensitive information, prevent financial losses, and ensure smooth business operations. It also protects a company’s reputation and helps comply with data protection regulations.
Cyber threats are escalating at an alarming rate. Businesses across industries are investing heavily in cybersecurity to protect their digital assets, and this demand is creating high-paying job opportunities for professionals in the field.
Cybersecurity job openings are growing rapidly than other IT jobs, with a global shortage of 3.5 million cybersecurity experts. This makes cybersecurity one of the most lucrative and stable career paths in 2025. Is cybersecurity the right career for you?
This article explores career opportunities available in cybersecurity, highlighting the in-demand skills, potential career paths, and attractive benefits associated with this essential field.
Why Cybersecurity is a Growing Industry?
Cybersecurity is a rapidly growing industry due to several key factors:
Global Cybersecurity Market Growth
The global cybersecurity market is projected to grow from USD 193.73 billion in 2024 to USD 562.72 billion by 2032, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 14.3%. The rapid growth indicates the rising significance of cybersecurity in protecting digital assets.
Regulatory Requirements
Governments and industries are enforcing stricter regulations on data protection. Key regulations include:
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) – Singapore
- Cybersecurity Act 2018 – Singapore
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – European Union
- Cybersecurity Act – ASEAN countries
Businesses must comply with these regulations, leading to a higher demand for cybersecurity professionals who can ensure data protection and regulatory compliance.
Increasing Frequency of Cyberattacks
Industries like finance, healthcare, and technology are particularly susceptible to cyber threats, leading to a strong demand for cybersecurity professionals. These sectors invest significantly in safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining customer trust.
With the continued rise of digital services, e-commerce, and remote work, the volume of sensitive online data is growing rapidly. Organisations are facing an increased risk of cyberattacks, requiring more robust security measures and trained professionals to defend against evolving threats.
According to the Cyble Global Cyber Threat Intelligence Overview 2024 report, ransomware attacks surged across industries with over 2,600 incidents reported in sectors such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
(Source: Security Week)
Prime examples are major groups like LockBit and RansomHub, pushing the frequency of attacks to new heights. These groups operate under the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, where they develop ransomware tools and distribute them to affiliates who execute attacks.
With cyber threats escalating, organisations are willing to invest significantly in cybersecurity talent, offering attractive salaries and career growth opportunities. How much can cybersecurity professionals in Singapore expect to earn?
Let’s explore the salary ranges across different experience levels.
Salary Ranges for Cybersecurity Professionals in Singapore
In Singapore, the government has identified 11 industry sectors as Critical Information Infrastructure (CII) that must comply with the Cybersecurity Act to ensure national security.
These sectors, including banking, healthcare, energy, and telecommunications, depend on skilled cybersecurity professionals to protect sensitive systems safeguard sensitive systems and ensure compliance with regulations.
With the rising demand for cybersecurity expertise and a shortage of qualified professionals, salaries in the industry remain highly competitive, offering strong earning potential across various roles and experience levels.
For example: A Cybersecurity Analyst with relevant certifications can expect higher pay compared to those without. Additionally, professionals with 5-9 years of experience typically receive an average salary increment of 20-30%, while those with over 15 years of experience can earn upwards of SGD 350,000 annually.
Let’s break it down for a clearer picture:
Cybersecurity Salary Breakdown (2025 Estimations)
| Job Level | Job Title | Estimated Annual Salary (SGD) |
| Entry-Level (0-3 years) | Cybersecurity Analyst, SOC (Security Operations Centre) Analyst, IT Security Engineer | S$48,000 – S$79,766 |
| Mid-Level (3-7 years) | Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker), Cybersecurity Engineer, Incident Response Analyst, Cloud Security Engineer | S$75,000 – S$90,000 |
| Senior & Leadership Level (7+ years) |
Security Architect, Cybersecurity Manager, Risk & Compliance Manager, Threat Intelligence Analyst, Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Head of Cybersecurity, Director of Information Security |
S$120,000 – S$180,000 |
(Source: Glassdoor, Morgan Mckinley, Talent.com)
Salaries vary based on industry, organisation size, and specific skills, with finance, government agencies, and multinational tech companies generally offering the highest compensation.
The Impact of Certifications and Experience on Salary
Several key factors can significantly impact your earning potential in today’s competitive job market. Certifications, experience, skills, and the company’s size and industry are crucial in determining your salary.
Understanding how these elements affect your salary can help you strategically plan your career for maximum financial reward.
1. Certification
Certifications validate your expertise and can significantly enhance your market value. They show employers that you have specific skills and knowledge, which often leads to higher salaries.
For example, in the field of cybersecurity, certifications such as CISSP and CompTIA Security+ are highly respected and can lead to better job offers. The more specialised and advanced your certification, the higher your earning potential.
2. Experience
Experience significantly impacts salary; more years in a field typically leads to higher pay. With experience, individuals gain skills in handling security incidents, managing complex tasks, and leading teams —qualities that employers value.
3. Skills
Specific skills, particularly those that are in high demand, can significantly influence your earning potential. Being proficient in advanced tools, technologies, or methodologies can distinguish you from other candidates. Regularly updating and expanding your skill set helps you stay competitive in the job market and may lead to higher salaries.
4. Company Size and Industry
The size of the company and the industry it operates in can significantly affect salary levels. Larger companies often have more resources and can offer higher salaries. Additionally, industries experiencing rapid growth or high demand, such as tech and healthcare, tend to provide more competitive salaries to attract top talent.
Certifications and Specialisations to Boost Your Career
Cybersecurity is a dynamic and in-demand, offering diverse career paths. Certifications play a crucial role in validating your skills and knowledge, making you a more attractive candidate to employers.
Essential Certifications
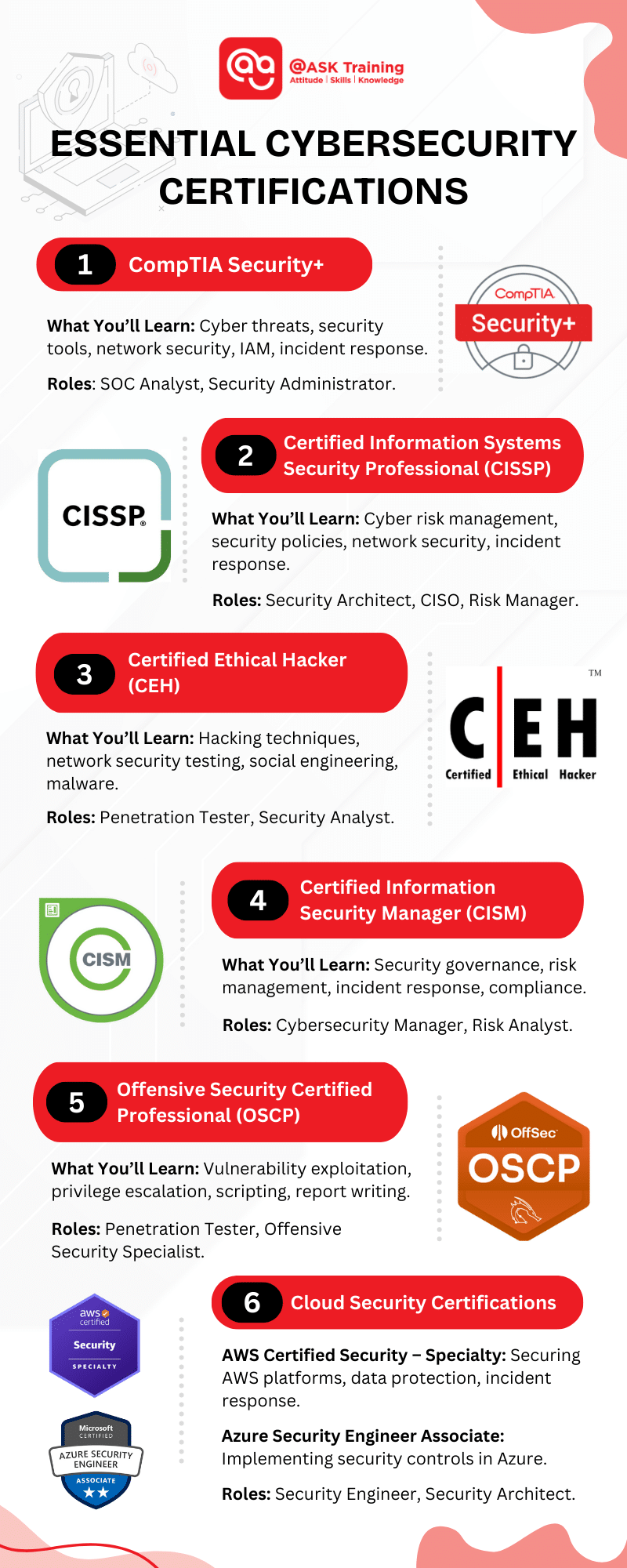
1. CompTIA Security+
The CompTIA Security+ certification is an ideal starting point for those entering the cybersecurity field. It provides recognition in the industry, fundamental cybersecurity knowledge, better job prospects, hands-on skills, and expertise not tied to any specific vendor. It’s also a stepping stone to more advanced certifications.
What You’ll Learn
- Cyber Threats & Attacks: Learn about hackers, malware, and phishing scams.
- Security Tools & Technologies: Understand firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption.
- Network Security: Protect computers and data from cyberattacks.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM): Learn how to keep user accounts secure.
- Incident Response: What to do if a cyberattack happens.
Key Benefits
- Industry Recognition: A globally recognised certification, often required for entry-level cybersecurity jobs.
- Higher Job Prospects: Many employers prefer or require Security+ for roles like SOC Analyst or Security Administrator.
- Vendor-Neutral Knowledge: Teaches general security concepts applicable to various technologies and platforms.
- Stepping Stone for Advanced Certifications: A foundation for pursuing CISSP, CEH, or OSCP.
2. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
The CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) certification is important because it is well-recognised in the industry and covers a wide range of cybersecurity topics. It is best suited for professionals aiming for management or architect positions.
What You’ll Learn
The course content for the CISSP certification includes:
- Cyber Risk Management: How to protect businesses from cyber threats.
- Security Policies & Compliance: Understanding security rules and laws.
- Network Security & Encryption: Keeping information safe from hackers.
- Incident Response & Recovery: Handling cyberattacks and protecting sensitive data.
Key Benefits
- High Demand: Required for many senior cybersecurity roles, including Security Architect, Risk Manager, and CISO.
- Salary Boost: CISSP-certified professionals earn 20–30% more than their non-certified peers.
- Global Recognition: Accepted by government agencies, MNCs, and top tech firms.
- Management & Leadership Focus: Ideal for those transitioning into cybersecurity leadership and governance roles.
Career Tip: CISSP requires five years of professional experience, but beginners can still take the exam and earn the Associate of (ISC)² certification, which is a great way to gain credibility.
3. Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
The CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) is important for beginners. CEH provides hands-on training in ethical hacking techniques, teaching professionals how to think like a hacker to find and fix security weaknesses before cybercriminals exploit them.
What You’ll Learn
The content of the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) course includes:
- Hacking Techniques: How hackers break into systems and how to stop them.
- Network Security Testing: Finding weaknesses in computer networks.
- Social Engineering: How hackers trick people into giving away sensitive information.
- Malware & Phishing Attacks: Understanding common cyber threats.
Key Benefits
- Opens Doors to Hacking Jobs: Qualifies you for roles like Penetration Tester and Security Analyst.
- Hands-On Learning: Focuses on real-world hacking techniques and security tools.
- Higher Salary Potential: CEH-certified professionals earn 10–20% more.
4. Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
The CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) certification is valuable for beginners due to its industry recognition. It builds a strong foundation in information security management, enhances career advancement, offers better pay, creates networking opportunities, and is applicable across various sectors.
What You’ll Learn
- Security Governance: Managing security policies and company rules.
- Cyber Risk Management: Identifying and reducing security risks.
- Incident Response & Recovery: Handling cyberattacks effectively.
- Compliance & Regulations: Ensuring companies follow security laws.
Key Benefits
- Pathway to Leadership: Helps you move into roles like Cybersecurity Manager or Risk Analyst.
- High Earning Potential: CISM holders often earn six-figure salaries.
- Recognised by Large Organisations: Required for many leadership positions in finance, healthcare, and government.
5. Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
The OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional) certification is valuable for beginners. OSCP is a highly technical certification focused on hands-on ethical hacking. Unlike CEH, which is more theoretical, OSCP requires practical application of penetration testing techniques in a real-world lab environment.
What You’ll Learn
- Vulnerability Scanning & Exploitation: Identifying weaknesses and gaining unauthorised access.
- Privilege Escalation: Moving from low-level access to full system control.
- Post-Exploitation Techniques: Maintaining access and covering tracks.
- Advanced Scripting & Automation: Using Python, Bash, and PowerShell for penetration testing.
- Report Writing & Documentation: Creating professional security assessment reports.
Key Benefits
- Highly Respected in the Industry: OSCP is a gold standard for penetration testing roles.
- Hands-On, Practical Focus: Requires real-world hacking scenarios and problem-solving.
- Competitive Salary Advantage: OSCP holders are in high demand and earn 30%+ more in offensive security roles.
6. Cloud Security Certifications
As businesses move towards cloud computing, specialised cloud security skills are also in high demand. Here are the top cloud security certifications you can consider:
AWS (Amazon Web Services) Certified Security – Specialty
This certification validates advanced skills in securing AWS platforms. It covers data protection, incident response, identity and access management, and infrastructure security. It’s recognised globally, emphasises practical experience, and enhances career prospects in roles like Security Engineer and Security Architect.
Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate
This certification validates the skills and expertise required to implement security controls, maintain the security posture, manage identity and access, and protect data, applications, and networks in Microsoft Azure environments.
While certifications validate your expertise, specialising in a specific cybersecurity domain enhances your career prospects and aligns you with industry demands.
Let’s explore further.
In-Demand Specialisations
Specialised expertise is also becoming more critical for businesses looking to protect their data and infrastructure. Below are some of the most in-demand cybersecurity specialisations, along with key roles and skills needed for each.
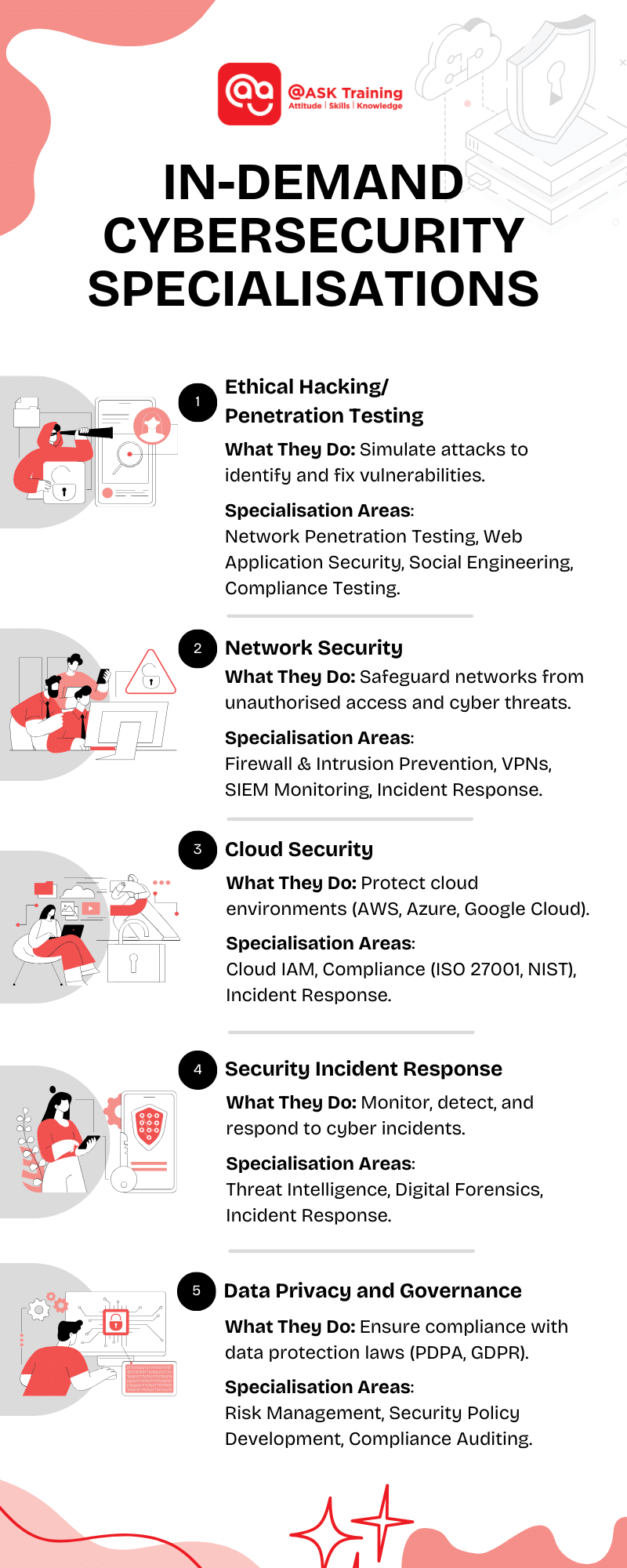
#1 Ethical Hacking/Penetration Testing
Penetration testers, often referred to as ethical hackers, are essential in the field of cybersecurity as they help organisations identify and fix security weaknesses before cybercriminals can exploit them. They simulate real-world attacks to test system defences, helping businesses strengthen their cybersecurity posture.
Specialisation Areas:
- Network Penetration Testing: Assessing vulnerabilities in corporate networks and infrastructure.
- Web Application Security: Identifying weaknesses in websites and applications.
- Social Engineering: Testing how easily employees can be manipulated into revealing sensitive information.
- Compliance Testing: Ensuring security policies meet regulatory standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Common Job Roles:
- Penetration Tester
- Ethical Hacker
- Security Analyst
- Vulnerability Assessor
- Assurance Validator
Key Skills Required:
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in programming languages (e.g., Python, C++), as well as familiarity with network protocols and operating systems.
- Problem-Solving: Ability to analyse situations and come up with creative ideas to identify and exploit vulnerabilities.
- Knowledge of Tools: Familiarity with penetration testing tools (e.g., Metasploit, Burp Suite).
Penetration testers play a vital role in keeping strong cybersecurity measures in place and protecting digital resources. Their efforts enable companies to stay proactive against cyber threats and maintain compliance with industry standards.
#2 Network Security
Network security experts work to safeguard an organisation’s network from unauthorised access, misuse, and cyber threats. They implement and oversee different security measures to maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data.
Specialisation Areas:
- Firewall & Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS/IDS): Configuring security controls to detect and prevent threats.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Securing remote access to corporate networks.
- Security Information & Event Management (SIEM): Monitoring security logs for suspicious activity.
- Incident Response: Developing action plans for network security breaches.
Common Job Roles:
- Network Security Engineer
- Network Security Administrator
- Security Operations Centre (SOC) Analyst
Key Skills Required:
- Technical Proficiency: Understanding of network protocols, firewalls, IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems), VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), and NAC (Network Access Control).
- Threat Detection and Response: Skill in identifying and addressing network threats and vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response: Ability to develop and execute plans for handling incidents.
Network security professionals play a pivotal role in safeguarding an organisation’s network infrastructure and ensuring the security of its digital assets.
#3 Cloud Security
Cloud security has become increasingly critical as organisations rapidly adopt cloud services. With more data and applications transitioning to the cloud, cloud security specialists protect data stored in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud from unauthorised access and cyber threats.
Specialisation Areas:
- Cloud Identity & Access Management (IAM): Controlling who can access cloud environments.
- Cloud Security Compliance: Ensuring cloud services comply with security frameworks (ISO 27001, CIS, NIST).
- Cloud Incident Response: Detecting and mitigating cloud-based cyberattacks.
Common Job Roles:
- Cloud Security Engineer
- Cloud Security Architect
- DevSecOps Specialist
Key Skills Required:
- Knowledge of Cloud Platforms: Skilled in using cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Security Frameworks and Standards: Understanding of frameworks such as ISO/IEC 27001, NIST, and CIS.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Expertise in managing user identities and access controls.
- Network Security: Skills in securing cloud network infrastructure.
- Incident Response: Ability to detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents.
- Encryption and Data Protection: Knowledge of encryption technologies and data protection methods.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Familiarity with regulatory standards and ensuring compliance.
The growing significance of cloud security requires professionals in this field to keep current with new technologies and threats to successfully protect the cloud environments.
#4 Security Incident Response
Organisations need 24/7 monitoring and rapid response to detect and contain security breaches. Security Operations Centre (SOC) professionals proactively track threats, while Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR) specialists investigate cyber incidents.
Specialisation Areas:
- Threat Intelligence & Malware Analysis: Understanding emerging cyber threats.
- Digital Forensics: Investigating security breaches to identify attack methods.
- Incident Response: Developing response plans for cybersecurity incidents.
Common Job Roles:
- SOC Analyst
- Incident Response Engineer
- Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR) Specialist
Key Skills Required:
- Threat Detection: Proficiency in identifying and analysing potential security threats.
- Investigation: Skills in conducting thorough investigations to understand the scope and impact of security incidents.
- Forensic Analysis: Knowledge of digital forensics to gather and analyse evidence related to security breaches.
- Incident Management: Expertise in managing and coordinating incident response efforts.
- Scripting and Automation: Ability to write scripts to automate incident response processes and improve efficiency.
- Knowledge of Security Tools: Familiarity with security information and event management (SIEM) systems, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and other security tools.
By staying vigilant and well-prepared, security incident responders play a vital role in protecting organisations from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
#5 Data Privacy and Governance
Data privacy has become significantly important due to regulations such as the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) in Singapore. These regulations ensure that organisations handle personal data responsibly, protecting individuals’ privacy and maintaining trust in online interactions.
Specialisation Areas:
- Risk Management: Assessing and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
- Security Policy Development: Creating security frameworks for organisations
- Compliance Auditing: Ensuring adherence to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Common Job Roles:
- Cyber Risk Manager
- Data Protection Officer (DPO)
- Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) Analyst
Key Skills Required:
- Knowledge of Data Protection Laws: Understanding regulations like PDPA, GDPR, and CCPA.
- Data Security: Implementing measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating data privacy risks.
- Analytical Skills: Analysing data privacy policies and practices for compliance.
How Certifications Demonstrate Expertise and Improve Job Prospects
Earning a certification can give you an advantage in your career by proving your skills, increasing credibility, and opening up more job opportunities.
Here’s how they can impact your career:
Validation of Skills
- Shows employers you meet industry standards and have the right knowledge.
- Acts as official proof from trusted organisations that you are qualified.
- Especially useful in cybersecurity, IT, finance, and healthcare, where up-to-date skills are crucial.
Increased Credibility
- Makes you more trustworthy to employers, clients, and colleagues.
- Demonstrates commitment to learning and professional growth.
- Helps you stand out in competitive job markets.
Improved Job Prospects
- Many companies prefer or require certifications for certain roles.
- Certified candidates often get priority in hiring and promotion decisions.
- Helps reduce employer risk, making you a stronger candidate.
Higher Earning Potential
- Certified professionals earn more than those without certifications.
- Employers are willing to pay more for specialised skills.
- Salary increases for certified professionals can range from 10% to 30%.
Earning certifications is a great first step in proving your skills and increasing job opportunities, but building a successful cybersecurity career requires more than just credentials.
Let’s explore the key steps to getting started in cybersecurity and securing your first job in the field.
How To Start Your Cybersecurity Journey
Embarking on a cybersecurity journey can be both exciting and rewarding.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Begin with Foundational Courses
IT Basics
Begin with fundamental Information Technology (IT) courses to build a strong technical foundation. This includes gaining an understanding of computer networks, operating systems, and basic programming.
Introductory Courses on Cybersecurity
Enrol in introductory courses specifically focused on cybersecurity. These courses will cover essential topics like threat detection, network security, and basic cryptography.
Step 2: Gain Hands-On Experience
Internships
Seek out internships in IT or cybersecurity to gain practical, real-world experience. Internships provide valuable insights into the industry’s workings and allow you to apply your knowledge professionally.
Virtual Labs and Simulations
Participate in cybersecurity labs and simulations. These controlled environments offer hands-on experience in detecting and mitigating security threats, which is essential for developing practical skills.
Online platforms offer virtual labs where you can practice security skills in a safe environment. Simulations such as Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions are also a great way to test your skills in areas like penetration testing, cryptography, and reverse engineering.
Personal Projects: Working on personal cybersecurity projects, such as setting up a home network with security measures or building a simple intrusion detection system, can provide valuable hands-on experience
Step 3: Take Tailored Training Courses
Several Continuing Education and Training (CET) Centres that are appointed by SkillsFuture Singapore (SSG) offer valuable training resources for aspiring cybersecurity professionals. They provide practical knowledge and skills essential to excelling in the cybersecurity landscape in Singapore.
Additionally, many of these courses may be eligible for funding through SSG, making cybersecurity training more accessible for beginners and career switchers.
Depending on your career goals, you might consider the courses covering topics like:
- Basic Cybersecurity Concepts: Ideal for newcomers to the field.
- Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing: This is for those looking to specialise in ethical hacking.
- Advanced Network Security: Suitable for professionals aiming to deepen their expertise.
For example, you can consider providers like @ASK Training Singapore that offer IT courses designed for both beginners and experienced professionals.
Most importantly, it is recommended to research different options available in Singapore and find a programme that aligns with your specific needs to be well-prepared for a successful career in cybersecurity.
Wrapping Up
With the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals will only continue to grow. This presents a unique opportunity for those seeking a challenging and rewarding career.
A career in cybersecurity offers several benefits that make it an attractive choice for many individuals. Here are the key takeaways:
- Significant Growth: The field is experiencing rapid expansion, with the global cybersecurity market projected to grow substantially in the coming years.
- High Demand: There is a significant demand for skilled professionals, leading to competitive salaries and job security.
- Meaningful Impact: Cybersecurity roles provide rewarding opportunities to protect sensitive information and combat cyber threats effectively.
Cybersecurity offers not only job security and competitive salaries but also the chance to contribute to a safer digital world.
Are You Ready to Kickstart Your Cybersecurity Journey?
To prepare for the future, @ASK Training provides practical, industry-relevant courses for both newcomers and seasoned professionals. Equip yourself with the skills you need to succeed in tomorrow’s cybersecurity landscape.
Here are some of our popular IT courses:
Explore our courses and start your journey today!
Related Courses
◆◆◆