Did you know in recent years, over 25% of businesses in Singapore have embraced cloud services outpacing growth in both the US and Western Europe, and this figure is projected to go further? Enterprises especially those with over 1,000 employees, have been particularly active in cloud adoption with over 94% utilising cloud-based solutions.
Cloud storage is a technology that allows you to store and access your data over the internet. Instead of storing your files on your local device (like your computer or phone), you store them on remote servers. This makes your data accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
In the current world dominated by data, cloud storage has become an essential tool for individuals and businesses alike. It offers a flexible, secure, and scalable solution to manage and access data across various fields, including IT, software development, and data analytics.
Given this strong foundation, understanding the fundamentals of cloud storage and learning how to choose the right service, you can significantly enhance your career prospects. This guide aims to provide you with the necessary knowledge and practical tips to effectively utilise cloud storage.
Let’s dive deeper into the practical applications of cloud storage.
Key Use Cases for Cloud Storage
Data Analytics and Data Lakes
Cloud-based data lakes are ideal for storing and managing massive datasets. They offer a centralised repository for data from various sources, such as social media, IoT devices, and business applications. By leveraging cloud storage, data analysts can efficiently:
- Cleanse and prepare data for analysis
- Apply advanced analytics techniques like machine learning and AI
- Generate valuable insights to inform decision-making.
For example, a researcher might store and analyse large datasets of scientific data, while a business analyst might use cloud-based data lakes to track sales trends and customer behaviour.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
One of the primary benefits of cloud storage is its ability to safeguard your data. By regularly backing up your files to the cloud, you can protect them from accidental deletion, hardware failures, or natural disasters. In the event of data loss, you can easily restore your files from the cloud.
Consider a student who stores their assignments and research papers on a cloud storage service. If their laptop crashes, they can retrieve their work from the cloud and continue their studies without interruption.
Development and Testing
Cloud storage provides a flexible and cost-effective platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. By storing code, libraries, and other development assets in the cloud, developers can:
- Collaborate with team members in real-time, regardless of location
- Access development tools and environments from anywhere in the cloud
- Quickly spin up and tear down development and testing environments as needed
For example, a software developer can use cloud storage to store their project code, test cases, and deployment scripts. They can then use cloud-based development tools to build and test their application, and finally deploy it to a cloud-based infrastructure.
Hybrid and Edge Computing
Hybrid cloud storage combines the benefits of on-premises storage and cloud storage. It allows you to store and process data locally while seamlessly integrating with cloud services for additional storage, computing power, and analytics capabilities.
Edge computing, a related concept, involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
For instance, a retail store might use edge computing to analyse customer data in real-time, while storing historical data in the cloud for long-term analysis.
Now that we’ve explored the key use cases let’s delve into the financial aspect of cloud storage.
Cost Management and Pricing Considerations
Cloud storage providers offer various pricing models to cater to different needs. Here are the primary ones:
On-Demand Pricing: This is a pay-as-you-go model, similar to renting a car. You pay for the storage and bandwidth you consume, making it ideal for unpredictable workloads.
Reserved Pricing: This model is like signing a lease. You commit to a specific amount of storage for a fixed term, often at a discounted rate. It’s suitable for consistent and predictable workloads.
Spot Pricing: This is a dynamic pricing model where you bid for unused computing resources, often at significantly reduced rates. It’s best for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
While these are the primary costs, it’s essential to be aware of potential hidden fees. These can include charges for:
- Data transfer: Moving data into and out of the cloud
- API requests: Frequent interactions with the cloud storage service
- Additional services: Features like data encryption, versioning, and lifecycle management.
To manage costs effectively, you can consider these strategies:
- Utilise cloud cost optimisation tools: These tools can analyse your cloud usage patterns and identify opportunities for savings.
- Implement FinOps practices: FinOps brings together finance, operations, and development teams to manage cloud costs proactively.
- Optimise storage tiers: Store frequently accessed data in faster, more expensive tiers, and infrequently accessed data in slower, cheaper tiers.
- Utilise data compression: Reduce storage costs by compressing data before storing it in the cloud.
- Monitor and analyse usage: Regularly review your cloud usage reports to identify areas for improvement.
Now that you understand the basics let’s dive into the practical steps of choosing the right cloud storage solution.
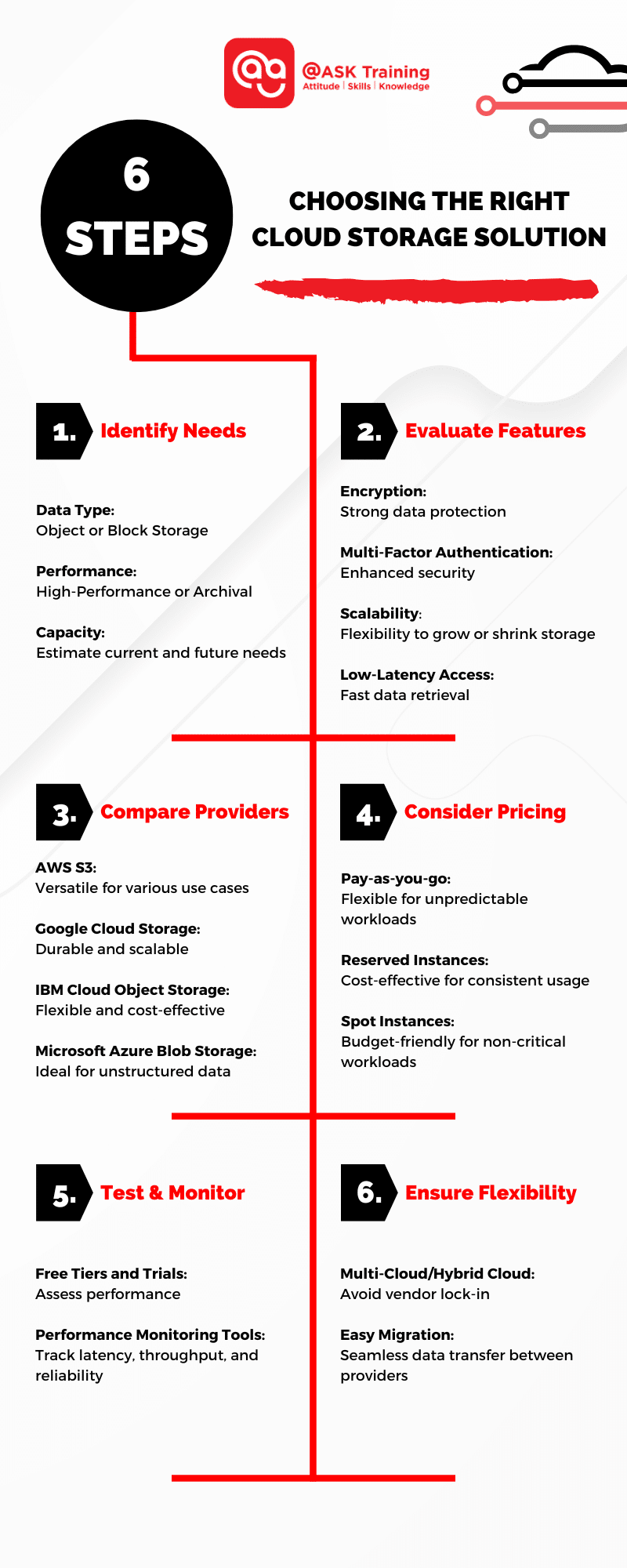
Step-by-Guide to Choosing the Right Cloud Storage Solution
To help you make an informed decision, let’s break down the process of selecting the right cloud storage solution into a few simple steps.
Step 1: Identify Your Storage Needs
The first step is to assess your specific storage requirements. Consider the following factors:
Data Type
Are you storing large, unstructured datasets like images, videos or documents (object storage) or structured, transactional data (block storage)?
For example, if you’re a photographer storing high-resolution images, you’ll need object storage, or if you’re a database administrator managing a relational database, you’ll need block storage.
Performance Requirements
Do you need high-performance storage for real-time applications or archival storage for infrequent access?
For a website or app that needs fast data access, you’ll need high-performance storage; however, if you’re using it for long-term backups or data archives, you can use cheaper, slower storage.
Storage Capacity
How much storage space do you need, and how quickly is it expected to grow? Estimate your current storage needs and consider future growth.
Step 2: Evaluate Key Features
Once you’ve identified your needs, look for cloud storage providers that offer the following key features:
- Data Encryption: Strong encryption ensures the security of your data both at rest and in transit.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: This adds an extra layer of security to protect your account.
- Scalability: The ability to easily increase or decrease storage capacity as needed.
- Low-Latency Access: Fast access to your data, especially critical for real-time applications.
Step 3: Compare Cloud Storage Providers
Several major cloud providers offer robust cloud storage solutions. Here are some of the leading options:
Offers a wide range of storage classes, including high-performance S3 and cost-effective S3 Standard-IA. A popular choice for storing large amounts of data, especially for websites and applications.
Provides durable and scalable object storage with strong security features. Offers a variety of options, including high-performance and low-cost storage.
Offers a variety of storage options, including high-performance and low-cost storage tiers.
Provides block blob, page blob, and append blob storage for various use cases. Ideal for strong large amounts of unstructured data, such as images, videos, and documents.
Step 4: Consider Pricing Structures
Cloud storage providers offer different pricing models, including:
- Pay-as-you-go: You pay for the storage and data transfer you consume. This would be best for unpredictable workloads or short-term projects.
- Reserved Instances: You commit to a specific amount of storage for a fixed term, often at a discounted rate. This is ideal for consistent, long-term workloads.
- Spot Instances: You bid on unused storage capacity, which can be significantly cheaper but less reliable. This would be a cost-effective option for non-critical workloads that can be interrupted.
Choose a pricing model that aligns with your budget and usage patterns.
Step 5: Test and Monitor Performance
Before fully committing to a cloud storage solution, consider using free tiers or limited trials to assess its performance. Monitor factors like latency, throughput, and reliability to ensure that the provider meets your needs.
Here are some easy-to-use tools to help assess performance:
- Ping (Built-In): Type ping [provider’s website] in your command prompt to measure response time.
- Speedtest by Ookla: Test upload and download speeds with files of different sizes.
- UptimeRobot: Monitor if the service stays online and alerts you if it goes down.
- File Transfer Test: Upload/download a file directly using the provider’s app to check speed and ease.
These tools can give you a clear idea of how well a cloud storage service will meet your needs, even if you’re just starting out.
Step 6: Ensure Long-Term Flexibility
Choose a cloud storage solution that supports easy migration and integration with other cloud services. Consider using a multi-cloud or hybrid-cloud approach to maximise flexibility and avoid vendor lock-in.
These steps can serve as a framework. Carefully consider your needs to select the right cloud storage solution to meet your business objectives.
Applications of Cloud Storage for Career Growth
Cloud storage is not just a technology. It’s a powerful tool that can significantly increase your career potential. The trend toward hybrid and multi-cloud strategies is also gaining momentum, with 67% of IT teams in Singapore currently utilising a combination of private cloud, public cloud, and on-premise infrastructure.
This number is expected to reach 91% in the near future, highlighting the flexibility and scalability benefits of such approaches. This further shows that mastering cloud storage concepts and skills can help position you for exciting opportunities in today’s data-driven world.
Here are the three main applications:
Multi-Cloud Expertise
Learning to work with multi-cloud storage platforms, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, can make you a highly sought-after IT professional. With multi-cloud expertise, you can:
Optimise Costs
Utilising the best pricing models and services from different providers. For example, you could store infrequently accessed data on a cheaper storage tier on one cloud provider, while running performance-critical workloads on a more expensive, high-performance tier on another.
Reduce Vendor Lock-In
Diversifying your cloud infrastructure can mitigate risks and improve flexibility. By spreading your workloads across multiple providers, you can avoid being tied to a single vendor and their pricing.
Enhance Disaster Recovery
Distributing workloads across multiple clouds can improve resilience and minimise downtime. If one cloud region experiences an outage, you can seamlessly fail over to another region or cloud provider.
Streamlined Development
Cloud storage plays a crucial role in modern software development. By storing code, artifacts, and test data in the cloud, development teams can:
Collaborate Seamlessly
Share code and work on projects together, regardless of location. For example, team members can access and work on the same codebase from anywhere in the world using tools like GitHub or GitLab.
Accelerate Development Cycle
Automated deployment pipelines can be set up to automatically build, test, and deploy code changes to production.
Reduce Infrastructure Costs
Utilise cloud-based development environments without the need for expensive hardware. Instead of buying and maintaining expensive servers, developers can utilise cloud-based virtual machines and containers.
Data Management
Cloud storage empowers data analysts and scientists to unlock valuable insights from massive datasets. By using cloud-based data lakes and warehouses, you can:
Store And Process Large Datasets
Handle petabytes of data efficiently. For example, you could analyse petabytes of customer data to identify trends and improve marketing strategies.
Perform Advanced Analytics
Utilise powerful tools and frameworks for machine learning, data mining, and business intelligence. You could use tools like Apache Spark or Databricks to build machine learning models and generate predictive insights.
Drive Data-Driven Decision-Making
Uncover trends, patterns, and anomalies to inform strategic decisions. By analysing data, you can identify opportunities for cost savings, improve operational efficiency, and develop new products and services.
Developing cloud storage skills will unlock numerous exciting career opportunities and contribute to the success of your organisation.
Let’s explore the next section on security and access control.
Security and Access Control
Cloud storage offers immense benefits, but it’s crucial to prioritise security to protect your valuable data. By understanding and implementing proper security measures, you can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your information.
Access Control
One of the fundamental aspects of cloud storage security is access control. This involves managing who can access your data and what actions they can perform. Here are some common access control mechanisms:
Signed URLs: These are time-limited URLs that grant temporary access to specific files or objects. They’re useful for sharing files with external parties without exposing your entire storage bucket.
Access Control Lists (ACLs): ACLs allow you to define granular permissions for individual users or groups of users. You can grant permissions like read, write, and delete access to specific files or folders.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM provides a centralised way to manage user identities and control access to your cloud resources. By using IAM, you can create users, assign roles, and implement multi-factor authentication.
Avoid Public Write Permissions
A common security mistake is granting public write permissions to your storage buckets. This means anyone on the internet could potentially upload malicious files or overwrite your data.
To prevent this, always adhere to the principle of least privilege: Grant only the minimum necessary permissions to users and applications.
You can protect your data from unauthorised access and ensure the integrity of your cloud storage environment by following these security best practices.
Wrapping Up
Cloud storage has revolutionised data management, offering flexibility, scalability, and security. By understanding its core principles and best practices, you can utilise this powerful technology to advance your career, protect your data, and streamline your workflows.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud storage is a versatile tool for storing and accessing data over the internet.
- Key use cases include data analytics, backup and disaster recovery, development and testing, and hybrid computing.
- Cost management is crucial, with pricing models like pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot pricing.
- Security is paramount. Implement access controls, avoid public write permissions, and stay updated on security best practices.
- Choosing the right cloud storage solution involves considering factors like data type, performance requirements, and pricing.
Whether you’re a student, developer, IT professional or data analyst, cloud storage skills are popular by demand. By honing your expertise in cloud storage solutions like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, you’ll be well-positioned for exciting opportunities in today’s data-driven world.
Don’t be intimidated by the vastness of the cloud. Start small by experimenting with free tiers offered by these major cloud providers. Explore their user-friendly interfaces and discover how cloud storage can simplify your data management tasks.
Ready to Take Control of Your Data?
Consider enrolling in our comprehensive Cloud Computing course! Our expert instructors are ready to equip you with the knowledge and skills to master cloud storage and unlock its full potential,
The future of data lies in the cloud. Get in touch with us to know more, and start your cloud journey today!
Related Courses
◆◆◆