Cloud infrastructure has become an essential component of modern businesses, offering a scalable, flexible, and cost-effective platform for delivering applications and services.
In Singapore, the cloud market is thriving, driven by the government’s strong support and the country’s strategic location. Our country has solidified its position as a leading hub for cloud infrastructure, attracting major tech companies that are making significant investments.
Let’s take a closer look.
Major Investments in Singapore’s Cloud Infrastructure
In 2024, major tech giants have continued to invest heavily in Singapore’s cloud infrastructure:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS has announced plans to invest an additional SGD 12 billion (approximately USD 9 billion) in its cloud infrastructure in Singapore from 2024 to 2028. This investment is expected to create thousands of jobs and contribute significantly to Singapore’s GDP.
- Google: Google has also increased its investment in Singapore’s digital infrastructure, committing USD 5 billion, which includes the completion of its fourth data centre in the country. This expansion reflects the high demand for cloud services in the region.
- Microsoft: Microsoft has been a major investor in Singapore’s cloud infrastructure, expanding its Azure services and partnering with local organisations to enhance digital transformation. This investment reflects the growing demand for cloud services in the region and demonstrates Microsoft’s commitment to supporting Singapore’s digital economy.
This surge in cloud adoption presents a wealth of opportunities for professionals looking to build successful careers in the tech industry.
With a clear grasp of Singapore’s cloud infrastructure landscape, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of cloud infrastructure. This includes key concepts, emerging trends, best practices, and valuable resources to help you make informed decisions for your business.
Understanding Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure refers to the underlying hardware and software that enables cloud computing services. It provides a scalable and flexible platform for businesses to access resources like storage, computing power, and networking capabilities on demand. This eliminates the need for organisations to invest in and manage their IT infrastructure.
Key Components of Cloud Infrastructure
- Data Centres: Physical facilities that house servers, storage devices, and networking equipment.
- Virtualisation: The technology that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, enhancing resource utilisation.
- Networking: The infrastructure that connects data centres and users, enabling data transmission and communication.
- Storage: The systems used to store data, including object storage, block storage, and file storage.
- Security: The measures implemented to protect cloud environments from unauthorised access and cyber threats.
Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure offers a wide range of benefits for businesses, including:
High Availability
Focuses on ensuring maximum availability, regardless of disruptions or events that may occur. For example, AWS offers multiple Availability Zones within each region, providing redundancy and fault tolerance.
Scalability
Cloud infrastructure can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing business needs, ensuring you always have the right resources. For example, Azure allows you to automatically scale your virtual machines based on workload demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Reliability
Designed to provide a reliable and resilient infrastructure. A system to recover from failure and continue to function. For example, the Google Cloud Platform offers features like automatic failover and replication to minimise downtime in case of failures or disasters.
Elasticity
Cloud services can automatically scale to acquire more resources when workloads increase, and they can release resources when they are no longer needed. For instance, AWS Lambda enables you to run serverless functions that scale based on demand, eliminating the need to manage infrastructure.
Predictability
Predictability in the cloud lets you move forward with confidence. Predictability can be focused on performance predictability or cost predictability. As an example, Azure Reserved Instances provide a discounted pricing model for long-term commitments, while AWS Spot Instances offer a cost-effective option for non-critical workloads.
Security
The different services allow you to control the amount of security responsibilities that you want to perform. If you prefer to have more control over the OS and patches, then the IaaS solution will suit you. If you prefer to perform lesser security work, then PaaS, SaaS, or other forms of solution might be more suitable.
Governance
You can create set templates to help ensure that all your deployed resources meet corporate standards and government regulatory requirements. Cloud platforms, such as Azure, often provide built-in auditing capabilities that can help you track resource usage, identify non-compliant configurations, and implement remediation strategies.
Manageability
Cloud platforms offer a variety of management tools to help you efficiently manage your cloud resources. The choice of tools depends on the preferences and skills of your administrators and the specific requirements of your organisation. For example, Azure provides a variety of management tools, such as the Azure Portal, Azure CLI, and Azure PowerShell.
Now that we have a solid understanding of cloud infrastructure, let’s explore the emerging trends shaping the industry.
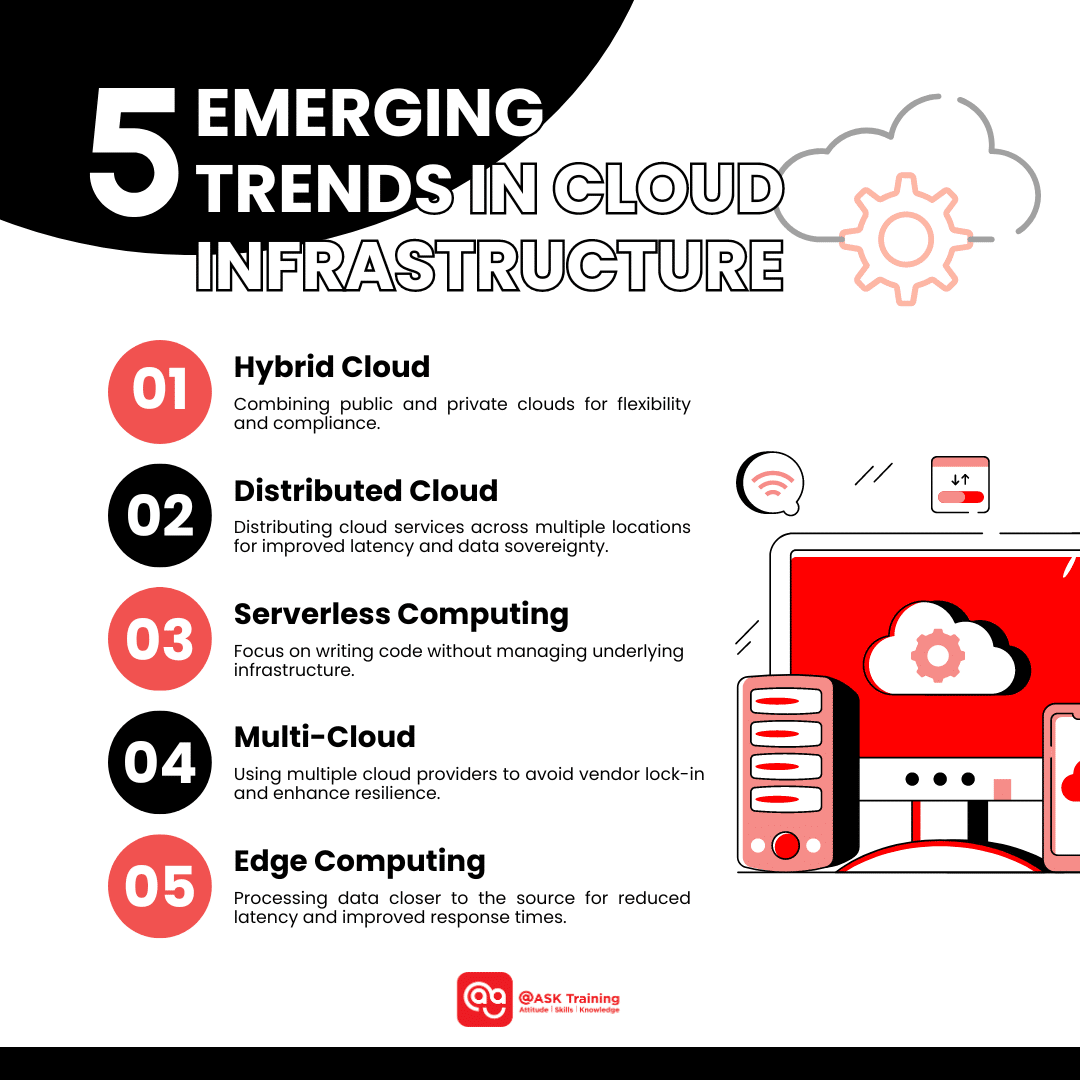
Emerging Trends in Cloud Infrastructure
Several trends are shaping the future of cloud infrastructure. These include:
Hybrid Cloud
Combining public and private clouds to leverage the best of both worlds. Hybrid clouds offer flexibility, scalability, and the ability to meet specific compliance requirements. For example, a business might use a public cloud for non-sensitive data and a private cloud for highly confidential information.
Distributed Cloud
Distributing cloud services across multiple geographic locations to improve latency, reliability, and data sovereignty. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with a global footprint or that need to comply with data residency regulations.
Serverless Computing
A model where developers can focus on writing code without managing underlying infrastructure. Serverless functions are automatically scaled based on demand, reducing operational overhead. This is ideal for event-driven applications and can significantly simplify development and management.
Multi-Cloud
Using multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in, enhance resilience, and leverage specialised services. By diversifying cloud usage, businesses can reduce their reliance on a single provider and improve their overall flexibility.
Edge Computing
Processing data closer to the source reduces latency and improves response times in IoT and real-time applications. Edge computing is particularly valuable for applications that require low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, smart city initiatives, and augmented reality.
Understanding the benefits and emerging trends of cloud infrastructure is essential, but it’s equally important to be aware of the security challenges it presents.
Key Security Challenges in Cloud Infrastructure
Despite the benefits it offers, cloud infrastructure also presents unique security challenges:
- Large Attack Surface: Cloud environments often have a vast attack surface due to the interconnected nature of services and components. This makes it challenging to protect against all potential threats.
- Lack of Visibility: Organisations may struggle to maintain visibility into their cloud infrastructure, making it difficult to detect and respond to threats. This can be exacerbated by the complexity of cloud environments and the use of multiple cloud providers.
- Complexity: The complexity of cloud environments, with multiple interconnected components, can make it challenging to manage security effectively. This requires a deep understanding of cloud security best practices and the use of appropriate tools and technologies.
- Human Factor: Insider threats and accidental employee errors can pose significant security risks. It’s essential to implement strong access controls and security awareness training to mitigate these risks.
- Shadow IT: Unauthorised use of cloud services by employees can introduce vulnerabilities and compliance risks. Organisations should establish clear policies and guidelines for cloud usage to prevent shadow IT.
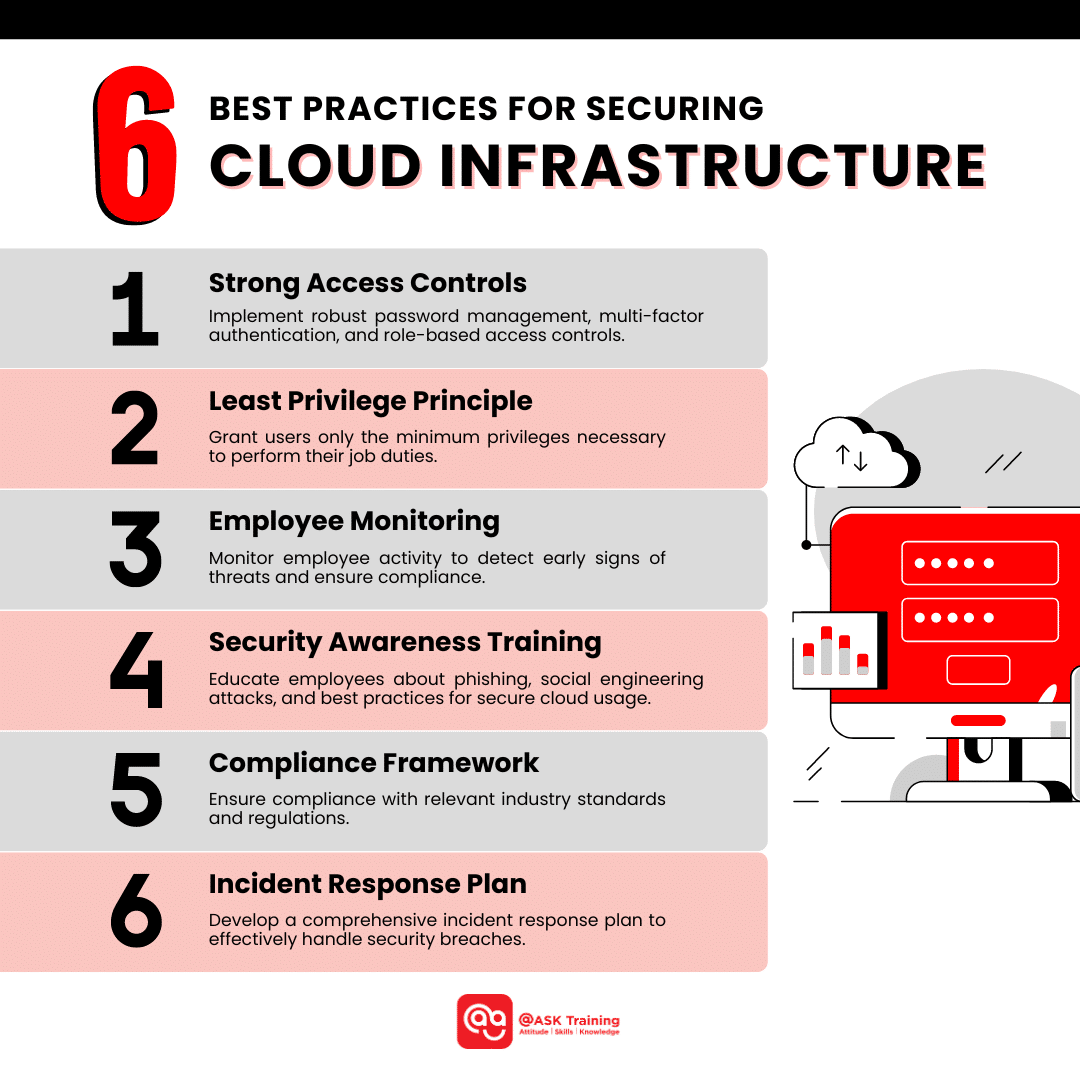
6 Best Practices for Securing Cloud Infrastructure
To mitigate security risks and protect your cloud environments, you can adopt the following cloud infrastructure best practices:
Strong Access Controls
Implement robust password management, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls to restrict unauthorised access.
Least Privilege Principle
Grant users only the minimum privileges necessary to perform their job duties. This helps to reduce the potential impact of data breaches and security incidents.
Employee Monitoring
Monitor employee activity to detect early signs of threats and ensure compliance. This can include monitoring network traffic, log files, and user behaviour.
Security Awareness Training
Educate employees about phishing, social engineering attacks, and best practices for secure cloud usage. Regular training can help employees identify and avoid potential security threats.
Compliance Framework
Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations of your respective countries, such as:
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) Singapore
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) EU
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIIPA) US
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
This can help to protect your business from legal and financial risks.
Incident Response Plan
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to effectively handle security breaches. A well-prepared incident response plan can help to minimise the impact of security incidents and restore operations quickly.
By implementing these best practices, you can enhance the security of your organisation’s cloud infrastructure and protect your critical assets from potential threats.
Remember, cloud infrastructure security is a shared responsibility, and a proactive approach is essential for maintaining a secure cloud environment.
The Role of AI in Cloud Infrastructure Management
In Singapore, artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a pivotal role in enhancing cloud infrastructure, driven by significant investments and strategic initiatives aimed at fostering innovation and digital transformation.
AI can:
- Automate Tasks: Streamline routine tasks, reducing human error and improving efficiency. For example, AI can be used to automate tasks such as provisioning resources, patching systems, and monitoring performance.
- Detect Anomalies: Analyse large datasets to identify unusual patterns that may indicate security threats. AI can detect anomalies that human analysts may miss, helping to improve security.
- Predict Failures: Use predictive analytics to identify potential issues before they occur, minimising downtime. AI can analyse historical data to identify patterns and predict potential failures, allowing organisations to take proactive steps to prevent them.
- Optimise Resource Allocation: Automatically adjust resource allocation based on demand, reducing costs and improving performance. AI can help to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and that costs are minimised.
Now that we have explored the key aspects of cloud infrastructure, let’s discuss how to get started!
Getting Started with Cloud Infrastructure
To embark on your cloud journey, here are a few general steps you can take to get started:
- Assess Your Business Needs: Determine your organisation’s specific requirements and goals for using cloud infrastructure. Consider factors such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, compliance requirements, and performance needs.
- Choose a Cloud Provider: Select a cloud provider that aligns with your business needs and offers the services you require. Major cloud providers in Singapore include AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Develop a Migration Strategy: Create a plan for migrating your existing applications and data to the cloud. This may involve a phased approach or a big bang migration, depending on your organisation’s specific circumstances.
- Implement Security Measures: Ensure that your cloud environment is adequately secured to protect sensitive data. This includes implementing strong access controls, monitoring for threats, and complying with relevant regulations.
- Monitor and Optimise: Continuously monitor your cloud infrastructure performance and make necessary adjustments to optimise resource utilisation and costs. This can be done using cloud monitoring tools and analytics.
Wrapping Up
Cloud infrastructure continues to evolve rapidly, presenting both opportunities and challenges. By understanding the key concepts, emerging trends, and best practices, you can make informed decisions about your cloud journey and position your business for success in the digital age!
For more information on cloud infrastructure and security, you can explore these resources:
- Cloud Security Alliance
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA)
- Government Technology Agency (GovTech)
- Centre for Strategic Infocomm Strategies
- Cybersecurity Agency of Singapore (CSA)
Ready to Upskill Your Team?
To support your cloud journey, consider @ASK Training as your ally and partner in upskilling! We offer comprehensive IT courses designed to equip you and your team with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in the cloud era.
Some of our popular IT courses include:
Contact us today to learn more about our cloud computing courses and how we can help your business succeed in the digital age!
Related Courses
◆◆◆