In today’s tech-driven world, businesses are choosing multi-cloud strategies to make the most of what different cloud providers offer. But how do these different platforms, like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, work together seamlessly? That’s where multi-cloud interoperability comes in.
In this guide, we’ll break down multi-cloud interoperability into three key aspects: what it is, how it works, and why it matters.
What is Multi-Cloud Interoperability
Multi-cloud interoperability is the ability to make different cloud platforms work together as one cohesive system. Instead of juggling separate tools and services from providers like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, interoperability ensures they integrate seamlessly, allowing you to focus on achieving your goals without worrying about technical barriers.
Picture this: You’re building a house, and each cloud provider is a different contractor specialising in one aspect—plumbing, wiring, or interior design. Interoperability ensures that all these specialists collaborate smoothly to complete the house without miscommunication or delays.
This capability allows organisations to use the best tools from each provider without being tied to just one, giving them greater flexibility and efficiency.
Understanding what multi-cloud interoperability is lays the foundation, but how does this integration actually happen? Let’s explore the key tools and processes that make seamless collaboration between cloud platforms possible.
How Multi-Cloud Interoperability Works?
Making multiple cloud platforms work together may sound complex, but it’s achievable with the right tools and strategies. Here’s how it happens:
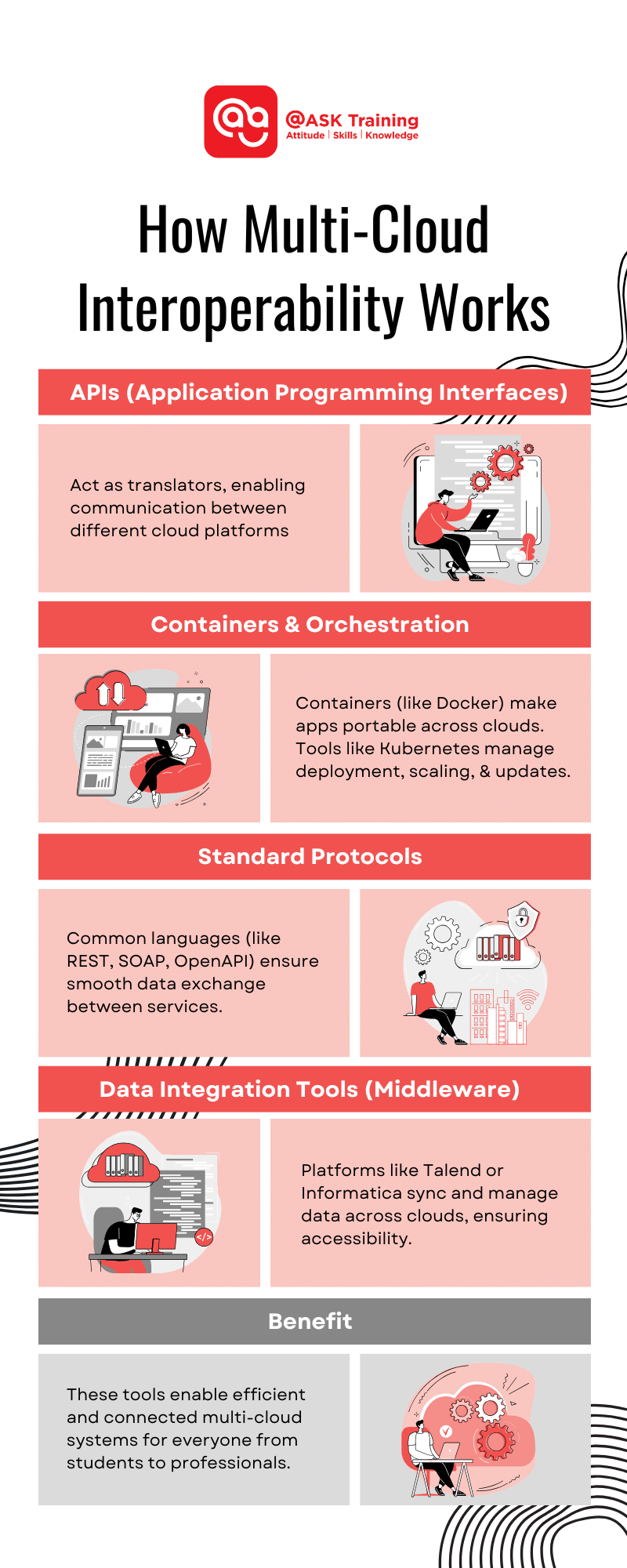
1. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
APIs act like translators, enabling cloud platforms to “talk” to each other. For instance, an Azure application might use APIs to access data stored on AWS, ensuring smooth communication.
Scenario: A food delivery app uses APIs to connect its Google Cloud-based order tracking system with an AWS-powered payment processing platform, making sure smooth coordination between the two systems.
2. Containers and Orchestration Tools
Docker Desktop
(Source: Docker)
Containers, like those powered by Docker, make applications portable across different cloud environments. Tools like Kubernetes orchestrate these containers, managing deployment, scaling, and updates effortlessly, regardless of the cloud platform.
Scenario: A video streaming company uses containers to host its app on Google Cloud but deploys additional resources on AWS during peak viewing hours. Tools like Kubernetes ensures the app runs smoothly across both platforms.
3. Standard Protocols
Protocols such as REST, SOAP, and OpenAPI create a common language for data exchange, ensuring smooth compatibility between cloud services.
Scenario: A healthcare provider uses standard protocols to securely transfer patient data from an on-premises system to Microsoft Azure for analytics, making the data accessible without having compatibility issues.
4. Data Integration Tools (Middleware)
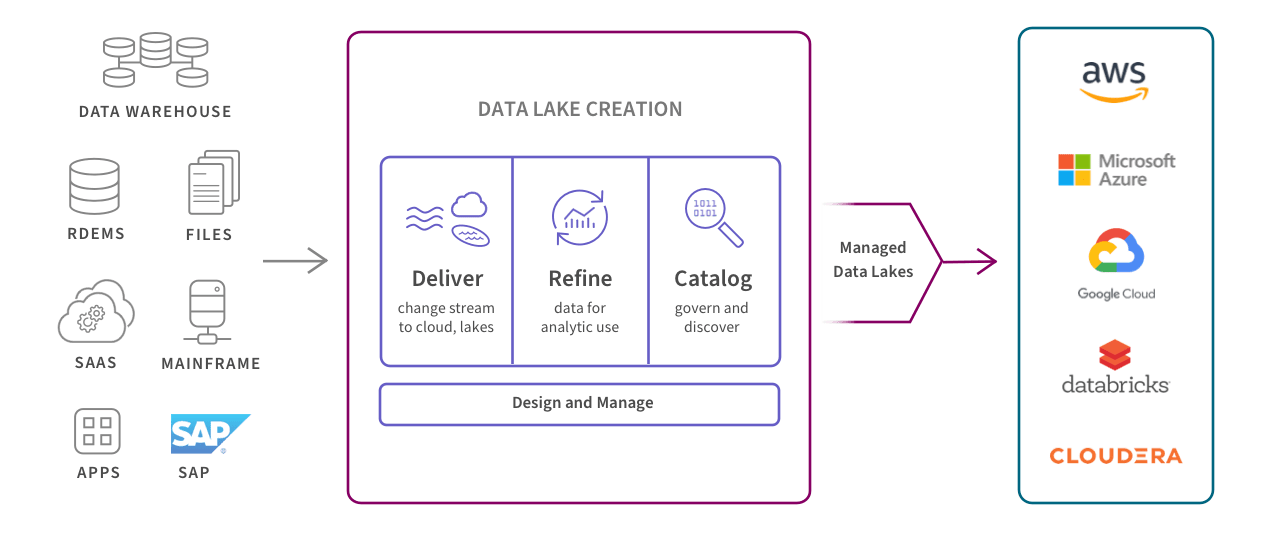
Example of Data Ingestion via Talend
(Source: Qlik)
Specialised platforms like Talend or Informatica help sync and manage data flows across clouds. This ensures that your data remains accessible and usable, no matter where it’s stored.
Scenario: A retail chain integrates sales data from AWS and inventory records from Google Cloud, allowing store managers to monitor stock levels and reorder ahead.
With these tools, anyone from IT students to cloud professionals can build a connected, efficient multi-cloud system that works smoothly across providers.
Now that we’ve covered how multi-cloud interoperability works, you might be wondering why businesses and IT professionals invest in this approach.
The answer lies in the practical benefits and opportunities it creates, which can transform both operations and outcomes.
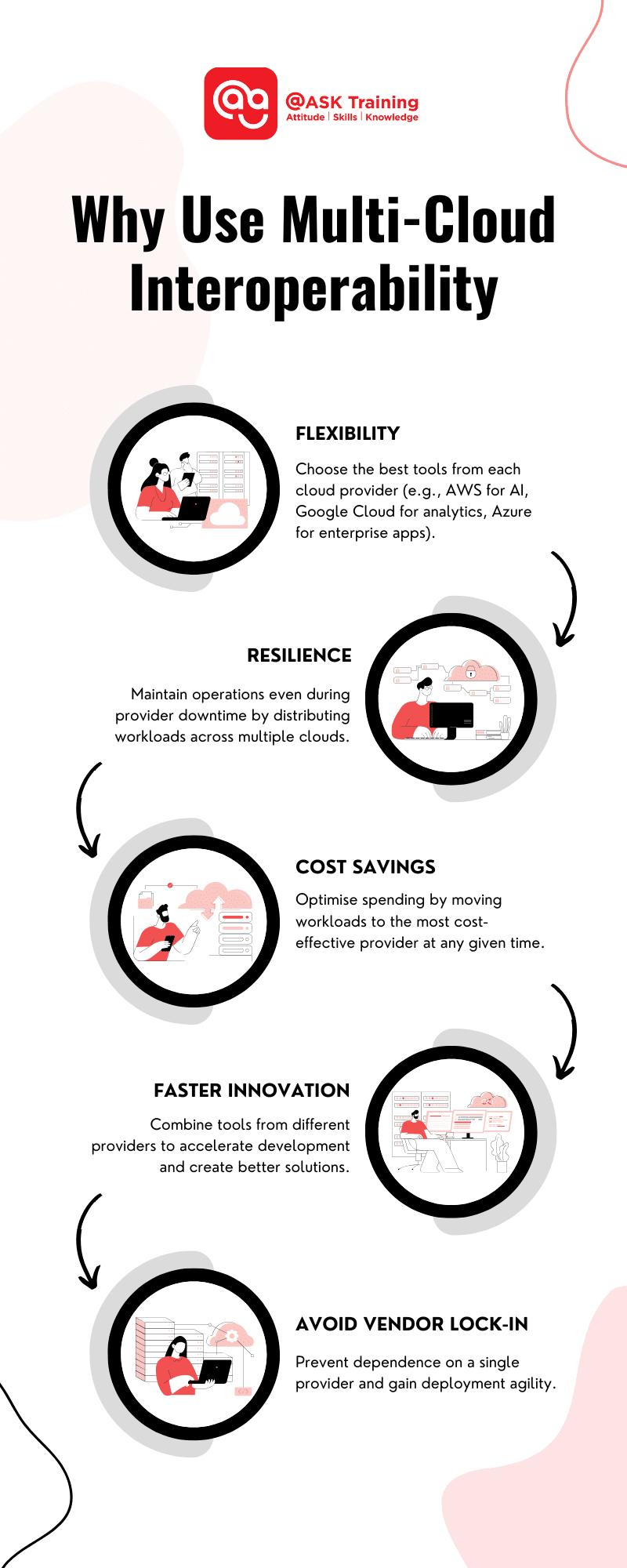
Why Multi-Cloud Interoperability is Used?
Businesses use multi-cloud interoperability to stay agile, reduce risks, and make the most of their technology investments. Here’s why it’s so valuable:
#1 Flexibility to Choose the Best Tools
Each cloud platform has its strengths. Interoperability lets businesses mix and match, such as using AWS for AI development, Google Cloud for advanced analytics, and Azure for enterprise apps—all working together seamlessly.
#2 Resilience and Reliability
By spreading workloads across multiple clouds, companies can keep things running even if one provider experiences downtime. This reduces disruptions and keeps operations on track.
#3 Cost Savings
Interoperability allows organisations to move workloads to the most cost-effective provider. For example, they can use AWS for high-demand periods and switch to a cheaper option during quieter times.
#4 Faster Innovation
With interoperability, teams can combine tools from different providers to create better solutions. Imagine developing an app with Kubernetes that pulls data from both Azure and Google Cloud—it speeds up development and expands possibilities.
#5 Avoid Vendor Dependence
Liberate the team from reliance on a single provider and gain the agility to deploy quickly anywhere.
This approach empowers you to adapt quickly and optimise resources, ensuring your strategies remain innovative, efficient, and future-ready.
The advantages of multi-cloud interoperability aren’t just theoretical—they’re actively shaping how organisations operate today.
Let’s take a look at some real-world scenarios where this approach is making a tangible difference.
Multi-Cloud Interoperability Real Life Applications
Multi-cloud interoperability isn’t just a concept—it’s transforming how organisations operate across industries.
Here are some real-world applications that demonstrate its value:
1. Hybrid Cloud Solutions for Business Continuity
Many businesses combine on-premises systems with public cloud platforms for added flexibility and reliability.
For example, a financial institution like JPMorgan may store sensitive customer data on a private cloud for security while using AWS or Google Cloud for customer-facing applications.
Multi-cloud interoperability ensures these systems communicate seamlessly, maintaining performance and compliance even during outages or peak loads.
2. E-Commerce Platforms Handling Traffic Spikes
Online retailers often face unpredictable traffic, especially during sales or holidays. By integrating multiple cloud providers, an e-commerce business can handle sudden surges effectively.
For instance, Shopify relies on a multi-cloud setup to ensure its merchants’ websites perform seamlessly during events like Black Friday. They use AWS for scalability and Google Cloud for analytics. This ensures a smooth shopping experience for customers, even under heavy demand.
3. Global Operations with Regional Compliance
Companies operating across multiple countries must comply with data residency laws, which require storing data within specific geographic regions.
A multinational corporation like Unilever operates in over 190 countries and uses a multi-cloud strategy with Microsoft Azure, AWS, and regional cloud providers to comply with local regulations.
Multi-cloud interoperability allows these systems to collaborate, ensuring global operations while meeting local legal requirements.
4. Seamless Development and Testing
Developers benefit from interoperability when building and testing applications across platforms.
For example, Spotify uses Kubernetes to manage its containerised applications, allowing their development teams to scale efficiently across Google Cloud and other providers. This flexibility accelerates the development cycle, allowing teams to deploy updates faster and more efficiently.
5. Disaster Recovery and Backup
Businesses often use multiple clouds to enhance their disaster recovery strategies. By storing backups on separate platforms, such as AWS and Google Cloud, they reduce the risk of data loss.
For example, Netflix employs a multi-cloud disaster recovery strategy by leveraging AWS and Google Cloud to ensure uninterrupted streaming services, even during provider outages.
Multi-cloud interoperability ensures these backups are easily accessible and can be restored quickly, minimising downtime and protecting critical information.
By applying multi-cloud interoperability in these ways, you will improve reliability, enhance compliance, and drive innovation. This approach keeps you and your organisation flexible and ready to thrive in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Wrapping Up
Multi-cloud interoperability is a game-changer in today’s digital landscape. It empowers you to:
- Integrate the best features of different cloud platforms
- Ensuring flexibility in choosing the right tools
- Resilience against downtime
- Cost savings through smarter workload distribution
- And faster innovation through seamless collaboration.
As IT professionals, students, and business leaders, adopting this approach positions you to thrive in a competitive and ever-evolving cloud ecosystem. Now is the time to explore how this approach can transform the way you work!
Take the Next Step
@ASK Training is here to help IT professionals and students like you stay ahead in cloud computing. Explore our 5-Day Cloud Computing course and gain knowledge in multi-cloud strategies.
If you’re new to the IT industry or looking to build a strong foundation in technology, check out our IT Foundations courses that are designed to help you start your journey with confidence and essential skills!
Get in touch with us today!
Related Courses
- Cloud Computing
- IT Foundations Courses
- Advanced Certificate in Infocomm Technology (Infrastructure and Operations)
◆◆◆