Gone are the days of trusting everyone “inside the castle walls.” In today’s dynamic cybersecurity landscape, threats can originate anywhere – even from seemingly authorised users. This is where Zero Trust Security steps in, offering a robust framework for protecting your organisation’s critical data and infrastructure.
Singapore’s Thriving Digital Landscape
As a global financial and technological hub, Singapore’s industries are increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure.
Key Industries in Singapore Benefiting from Zero Trust:
- Financial Services: Protecting sensitive financial data and preventing unauthorised access to customer accounts.
- Manufacturing and Logistics: Securing supply chains, IoT devices, and critical infrastructure.
- Healthcare: Safeguarding patient data and preventing breaches that could compromise healthcare services.
- Government: Protecting sensitive government information and ensuring national security.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to understand Zero Trust Security. We’ll delve into its principles, benefits, and implementation strategies, empowering you to adopt a more secure and future-proof approach to IT security.
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a security paradigm that challenges the traditional “castle and moat” model. Unlike traditional models that grant access based on location (inside the network perimeter), Zero Trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.”
This means every access request, regardless of user or device, is meticulously scrutinised before granting access to resources.
Here’s a table summarising the key differences between traditional security and Zero Trust:
| Feature | Traditional Security | Zero Trust Security |
| Zero Trust Model | Implicit trust within the network | Explicit verification for all access |
| User Access | Broad access based on location | Least privilege access control |
| Visibility | Limited visibility into user activity | Continuous monitoring and logging |
In today’s cloud-centric world, Zero Trust Security shines. As applications and data move beyond physical boundaries, Zero Trust ensures consistent protection regardless of location.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Security
With a clearer picture in mind, Zero Trust Security rests on several key principles:
- Continuous Verification and Monitoring: Zero Trust assumes a potential breach and constantly verifies user identities, devices, and access requests. This can involve Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and real-time access monitoring.
- Least Privilege Access: Users only have access to the specific resources they need to perform their job functions. This minimises the potential damage if a breach occurs.
- Device Access Control and Micro-Segmentation: Zero Trust restricts access based on device security posture and segments the network into smaller zones. This prevents attackers from moving laterally within the network and accessing sensitive data.
By combining these principles, Zero Trust creates a layered defence that significantly reduces the attack surface and strengthens your overall cybersecurity posture.
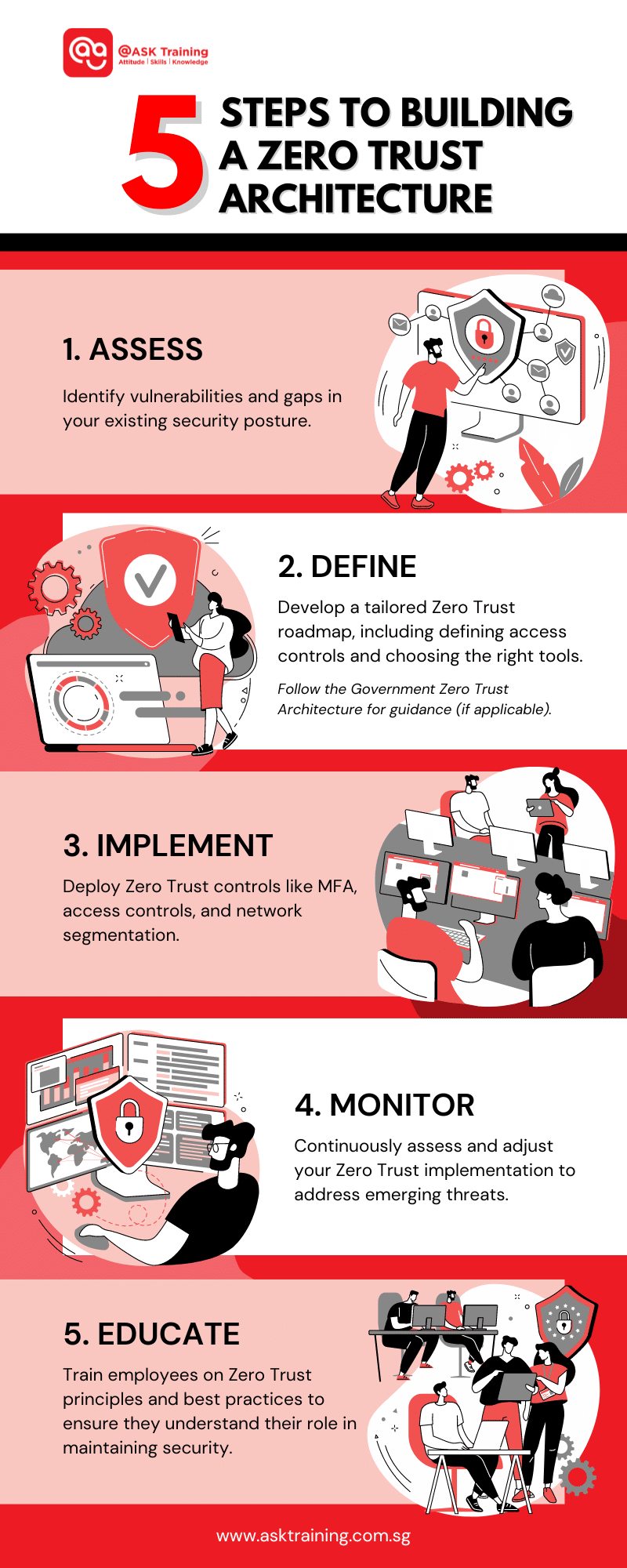
Steps to Building A Zero Trust Architecture
Equipped with the key principles, transitioning to Zero Trust requires a strategic approach. Here are some initial steps:
Step 1: Assess Your Current Security Posture
Identify existing vulnerabilities and gaps in your current security measures. A comprehensive risk assessment will identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. (Resource: How to perform a cybersecurity risk assessment step-by-step). This will help you tailor your Zero Trust implementation.
Step 2: Define Your Zero Trust Architecture
Research available technologies and best practices to develop a roadmap for building your Zero Trust environment. This involves identifying critical assets, defining access control policies, and choosing the right security tools.
If your business is based in Singapore, the Government Zero Trust Architecture (GovZTA) provides a valuable framework for guiding your Zero Trust implementation. The GovZTA outlines key principles and best practices to help you build a robust and effective Zero Trust architecture.
Step 3: Implementation
Begin implementing Zero Trust controls like MFA, access controls, and network segmentation. This may be a phased approach depending on your organisation’s needs.
Key Considerations for Implementation
- Technology Selection: Choose the right tools and technologies that align with the GovZTA framework and your organisation’s specific requirements.
- Policy Development: Create clear and comprehensive policies that define access controls, user behaviour, and device management.
- User Education and Training: Ensure that your employees understand the importance of Zero Trust and how to follow the established policies.
- Continuous Monitoring and Assessment: Regularly monitor your Zero Trust implementation to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.
Here’s a summary of the important steps to building a Zero Trust Architecture:
By following the GovZTA framework and carefully considering these factors, you can effectively build a Zero Trust architecture that strengthens your organisation’s security posture and protects against emerging threats.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
Now that we understand the steps needed to start implementing Zero Trust Security, let’s take a look at the numerous benefits it offers:
- Enhanced Security: By tightening access controls and verifying every request, Zero Trust makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain a foothold in your network.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Limiting access minimises the potential damage caused by a breach.
- Improved User Experience: Unlike traditional VPNs, Zero Trust can offer a seamless access experience for authorised users.
- Cloud Compatibility and BYOD Enablement: Zero Trust fosters secure access to cloud applications and facilitates Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies.
Examples of Zero Trust Security in Action
Zero Trust Security is increasingly being adopted across various sectors due to its effectiveness in mitigating cyber threats.
While specific case studies for each industry might be limited, here are some general examples of how Zero Trust Security is applied across different sectors:
Healthcare Industry
Protecting Patient Data
Healthcare organisations have utilised Zero Trust Security to safeguard sensitive patient information. By enforcing strict access controls and continuous monitoring, these organisations can secure remote access to data without the need for an internal IT team.
This approach not only protects against data breaches but also facilitates compliance with healthcare regulations.
For example, Stanford Healthcare (Medicine) implemented a Zero Trust framework to protect patient data and comply with HIPAA regulations. The hospital successfully prevented numerous cyberattacks and data breaches by enforcing strict access controls and continuous monitoring.
Financial Services
Safeguarding Customer Data
Organisations in the financial services industry have implemented Zero Trust to protect customer data from unauthorised access and prevent data breaches. By enforcing strong access controls and encrypting sensitive data, these organisations can maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and safeguard their customers’ financial information.
For example, JPMorgan Chase has adopted a Zero Trust approach to protect its customers’ sensitive financial data. The bank has implemented a variety of Zero Trust controls, including multi-factor authentication, micro-segmentation, and endpoint security, to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Public Sector
Protecting Critical Infrastructure
Government agencies have also embraced Zero Trust to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive data. By implementing Zero Trust principles, these agencies can reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with government security standards.
For example, The U.S. Department of Defence has been a pioneer in adopting Zero Trust principles to protect its critical infrastructure and sensitive data. The department has implemented a comprehensive Zero Trust framework that includes continuous monitoring, least privilege access, and micro-segmentation.
Technology and Manufacturing
Securing Intellectual Property
Technology and manufacturing companies have adopted Zero Trust to protect their intellectual property and prevent unauthorised access to sensitive data. By enforcing strict access controls and monitoring network activity, these organisations can safeguard their competitive advantage.
For example, Tesla has implemented a Zero Trust architecture to protect its intellectual property and prevent unauthorised access to its manufacturing facilities. The company has invested heavily in cybersecurity measures, including endpoint security, network segmentation, and threat detection.
Retail
Protecting Customer Data and Preventing Fraud
Retailers have implemented Zero Trust to protect customer data and prevent fraud. By enforcing strong authentication measures and monitoring for suspicious activity, retailers can safeguard their customers’ personal information and reduce the risk of financial losses.
For example, Target has adopted Zero Trust principles to enhance the protection of customer personal information. The retailer employs various security measures, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems, to prevent data breaches effectively
These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of Zero Trust Security across various industries. By adopting Zero Trust principles, organisations can significantly enhance their security posture and protect against emerging threats.
Wrapping Up
Zero Trust Security represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, offering a more robust and adaptable approach to protecting your organisation’s critical assets.
Key Takeaways:
- Never Trust, Always Verify: This is the core principle of Zero Trust, which emphasises continuous authentication and authorisation for all users, devices, and applications accessing resources.
- Least Privilege Access: Grant users only the minimum level of access needed to perform their tasks, reducing the potential damage from a compromised account.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor user activity, network traffic, and device health to detect suspicious behaviour and potential threats.
- Micro-segmentation: Divide networks into smaller, more secure zones to limit the impact of a breach and prevent lateral movement.
- Utilise the GovZTA Framework: In Singapore, the Government Zero Trust Architecture (GovZTA) provides a valuable framework for implementing Zero Trust.
- Tailor to Your Organisation: Implement Zero Trust to align with your organisation’s specific needs and industry requirements.
By embracing Zero Trust principles and implementing them strategically, you can significantly improve your security posture and stay ahead of evolving threats.
Ready to take the next step?
Explore further resources on Zero Trust implementation and consider professional training to equip your IT team with the necessary skills.
@ASK Training offers a range of full and modular IT courses, with up to 90% funding available depending on eligibility. Here are a few related IT courses you can explore:
- Enterprise Architecture and Design Course
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking
- Advanced IT Security and Cybersecurity
Get in touch with us today to provide your team with the knowledge and skills needed to construct a secure and robust IT infrastructure!
Remember, in today’s world, security is not a destination, but a continuous journey. By embracing Zero Trust Security, you can empower your organisation to navigate the modern threat landscape with confidence!
Related Courses
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking
- Enterprise Architecture and Design
- Advanced IT Security and Cybersecurity
◆◆◆