 In the last few years, interest in emerging technologies in IT has skyrocketed. From small start-ups to global enterprises, businesses are rapidly integrating new tech to stay ahead.
In the last few years, interest in emerging technologies in IT has skyrocketed. From small start-ups to global enterprises, businesses are rapidly integrating new tech to stay ahead.
In Singapore, government-led initiatives like Smart Nation and National AI Strategy 2.0 have further accelerated this trend, positioning the country as a regional tech hub.
As a result, the skills employers look for are evolving faster than ever, creating both challenges and exciting opportunities for aspiring IT professionals.
“Emerging technologies” describe cutting-edge innovations that are moving from labs and pilot projects into real-world business applications. They not only transform industries but also create brand-new job roles that didn’t exist a few years ago.
Whether you’re a university student, a recent graduate, or a mid-career professional looking to pivot, this guide will help you understand what’s coming, what skills you need, and how to prepare.
We’ll break down eight major technology areas shaping the future of IT and share practical steps to start building your expertise today, all while highlighting Singapore’s unique tech landscape.
Landscape of Emerging IT Technologies in 2025
By 2025, emerging technologies like generative AI and edge computing will become mainstream, while others will still be experimental but gaining momentum (such as quantum computing and spatial computing).
In Singapore, initiatives such as IMDA’s 5G innovation programmes and large-scale AI deployments by local companies like DBS and Grab reflect these trends.
Here’s a quick snapshot:
| Technology Domain | Adoption Stage | Talent Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Generative & Agentic AI | Mainstream | High |
| Quantum Computing | Experimental | Growing |
| Edge Computing & 5G | Scaling Fast | High |
| Spatial Computing (XR) | Early Adoption | Medium |
| Green IT & Sustainability | Scaling Up | High |
| Autonomous Robots | Early Growth | Medium |
| AI Governance & Trust | Emerging | Growing |
Local employers are looking not just for technical specialists, but for professionals who understand how to translate these innovations into real business value aligned with national strategies like Smart Nation and the Green Plan 2030.
By becoming an early adopter in these fields, you will be strategically positioned for leadership roles and high-impact projects, setting yourself apart in a competitive job market.
Generative & Agentic AI
Two rapidly evolving fields that are redefining how we interact with technology and create content: Generative and Agentic AI.
Generative AI refers to tools that can create new content – text, images, videos, or code, based on existing data. Think ChatGPT (text), Leonardo (images), or GitHub Copilot (code generation).
Agentic AI takes this further, enabling systems to act autonomously. For example, an AI agent that can analyse meeting notes, book appointments, or automate customer support conversations without direct human supervision.
This autonomy extends to critical development tasks. For example, an autonomous code-review tool can dramatically boost developer velocity and significantly reduce bugs by identifying issues proactively.
In Singapore, banks like DBS and OCBC are already deploying AI to enhance fraud detection, personalise customer experiences, and automate backend operations.
Why It Matters
Generative and agentic AI are actively reshaping roles in content creation, software engineering, customer support, marketing, and even product design. As these technologies become more integrated, professionals with the ability to design prompts, fine-tune models, and integrate these AI systems into existing workflows will be in high demand.
Core Skills To Learn:
- Prompt Engineering and Prompt Design: Learning how to craft effective instructions to guide AI models to produce desired outputs.
- Basic Model Fine-Tuning: Understanding how to adapt a pre-trained AI model to perform a specific task more effectively with new data.
- AI Governance and Ethics Fundamentals: Grasping the principles and frameworks for developing and deploying AI responsibly and ethically.
- Understanding API integrations with AI services: Knowing how to connect and utilise AI services within other applications and systems.
Action Step:
Get hands-on! Start experimenting with generative AI tools and build a small project. This could be a chatbot that handles common queries for a personal website or an AI-driven social media content generator.
Quantum Computing & Post-Quantum Security
Quantum computing promises to revolutionise computation by processing massive datasets exponentially faster than traditional systems. Qubits, the fundamental units of quantum computers, operate like light switches that can be on, off, or both at the same time, enabling complex problem-solving capabilities.
In Singapore, the National Quantum-Safe Network (NQSN) was launched to drive research and deployment of quantum-safe communication technologies, putting the country at the forefront of quantum security readiness in Asia.
Why Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Matters:
Organisations in finance, healthcare, logistics, and national security are actively investing in quantum research and quantum-safe security. This proactive approach is critical because quantum computers pose a real risk to today’s encryption methods.
If we don’t act early, the security protecting everything from bank transactions to government data could be compromised. Think of PQC as changing all the locks before quantum burglars exist. By upgrading our cryptography now, we safeguard critical systems for the future.
Developing early familiarity with PQC can strategically position you as a forward-thinking specialist.
Entry Pathways:
Quantum Computing Internships
- This pathway involves actively participating in the research and development of quantum algorithms, gaining hands-on experience with hybrid classical-quantum computing.
- Participating in quantum computing internships or hackathons, often run by universities like NUS and NTU, is a great starting point.
Post-Quantum Cryptography Migration
- This focuses on helping organisations transition their existing cryptographic systems to quantum-safe algorithms and contributing to cybersecurity initiatives implementing PQC standards.
Research and Development Roles
- These roles involve contributing to cutting-edge advancements through national or international collaborations and developing prototypes for quantum communication and encryption.
Beginner Quantum Programming Courses
- A foundational step, these courses are offered by major tech companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Google, providing an accessible entry point to learn quantum programming.
Advanced Connectivity & Edge Computing
The widespread rollout of standalone 5G Connectivity and upcoming 6G networks provides the high-speed, low-latency backbone necessary for edge computing to thrive. This powerful combination allows data from devices and sensors to be processed instantaneously at the “edge” of the network, close to where it is created, rather than being sent back to a distant cloud data centre.
Singapore’s nationwide 5G rollout, championed by IMDA, has enabled companies like Grab to enhance their delivery logistics and allowed hospitals, such as those under the National University Health System, to utilise 5G-powered mixed reality solutions to advance telemedicine, real-time surgical imaging, and remote diagnostics. (Source: SBR)
Why Edge and Advanced Connectivity Matter:
Industries from manufacturing to autonomous vehicles rely on ultra-fast, low-latency connections. For aspiring IT professionals, understanding how to architect, secure, and deploy robust edge solutions is not just beneficial—it’s crucial for future success. This capability supports real-time response for critical applications and enables scalable smart city planning.
Certifications to Consider
- Cisco DevNet (IoT and 5G tracks): Foundational and advanced skills for developing, securing, and deploying IoT and 5G-enabled edge solutions.
- AWS Certified Advanced Networking: Proficiency in designing and managing distributed, hybrid, and edge cloud architectures.
- Microsoft Azure IoT Developer Speciality: Focused on automating and integrating IoT and edge scenarios on the Azure platform, aligning with Singapore’s enterprise cloud adoption.
Action Step:
Explore edge-focused cloud services and start a small IoT project, like building a home automation sensor system or a simple supply chain tracker.
Spatial Computing & Extended Reality (XR)
Spatial computing merges physical and digital experiences, covering AR (augmented reality), VR (virtual reality), and MR (mixed reality). This creates immersive experiences that transform how we interact with information and environments.
AR adds digital layers to reality (like Pokémon GO). VR transports you to new worlds (like Beat Saber). MR blends both: imagine a surgeon practising with holograms that interact with the real operating room.
In Singapore, industries are actively embracing XR to enhance capabilities and engagement.
SIA-NUS Digital Aviation Corporate Laboratory (Source: NUS)
For example, Singapore Airlines has adopted VR to train pilots and cabin crew, enabling safe, realistic simulations that improve readiness and safety.
Meanwhile, local real estate developers are using AR tools to help potential buyers visualise properties in 3D before construction, improving decision-making and customer experience.
Why Spatial Computing Matters:
Sectors like healthcare, engineering, architecture, and entertainment are exploring spatial computing to improve design, training, and user engagement.
Core Skills to Develop
- Unity or Unreal Engine Development: Learn to build AR/VR applications using the leading real-time 3D development platforms.
- 3D Modelling and Animation: Acquire skills to create realistic objects and environments that bring experiences to life.
- Spatial UX Design: Understand how users interact with spatial interfaces to design intuitive, comfortable, and engaging experiences.
Action Step:
Start by creating a mini-demo using Unity or Unreal Engine, such as a basic AR or VR app project, like an interactive virtual showroom or a simple training simulation. Use this as a portfolio piece to showcase your ability to bring spatial concepts and tools to life.
Energy-Efficient & Green IT
With global data centres consuming massive amounts of energy, sustainability has become a priority for CIOs and CTOs. This is why forward-thinking leaders now meticulously track energy consumption per compute unit.
By understanding this metric, they can pinpoint inefficiencies and optimise operations, exploring innovative solutions like liquid-cooled or modular data-centre designs that drastically reduce energy waste and space.
Inspiring examples of this commitment to sustainable infrastructure include pioneering underwater or solar-powered data centre pilots that demonstrate the future of eco-friendly computing, such as Microsoft’s Project Natick. Although it ended in 2024, its research continues to influence future eco-friendly data centre designs globally.
In Singapore, the Green Plan 2030 pushes for energy-efficient IT practices, and data centres are being incentivised to improve their energy usage. For instance, AWS’s Well-Architected Framework includes a dedicated Sustainability Pillar that guides architects in designing low-energy, efficient cloud workloads.
Why Green IT Matters
Beyond compliance, green IT strategies reduce operating costs through improved energy efficiency. Sustainability is also a critical component of corporate responsibility and brand reputation in today’s market. IT professionals who understand and can implement green IT sustainability principles are invaluable, driving strategic value and aligning businesses with a sustainable future.
Learning Paths
Sustainable Cloud Architecture
Deepen understanding of sustainability pillars in cloud frameworks from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, focusing on workload efficiency, resource optimisation, and energy consumption metrics.
Energy-Efficient Data Centre Design
Study emerging trends, including liquid cooling, modular deployments, immersion cooling, and renewable energy integration.
Carbon Footprint Monitoring
Learn tools and methodologies for measuring and managing carbon emissions from IT operations, including scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions framework. You can start with UN Global Compact Singapore’s Carbon & Emissions Recording Tool (CERT) or Building Carbon Calculator.
Action Step:
Research and document how your current or future IT projects can strategically reduce energy use. Integrate these findings as a compelling part of your professional portfolio, showcasing your commitment to sustainable innovation.
Autonomous Systems & Polyfunctional Robots
Robots are evolving from performing single repetitive tasks to taking on multiple functions, such as a warehouse robot that can pick, pack, and conduct quality inspections all at once.
Singapore’s advanced manufacturing initiatives include deploying autonomous robots in warehouses and ports to improve efficiency and reduce reliance on manual labour.
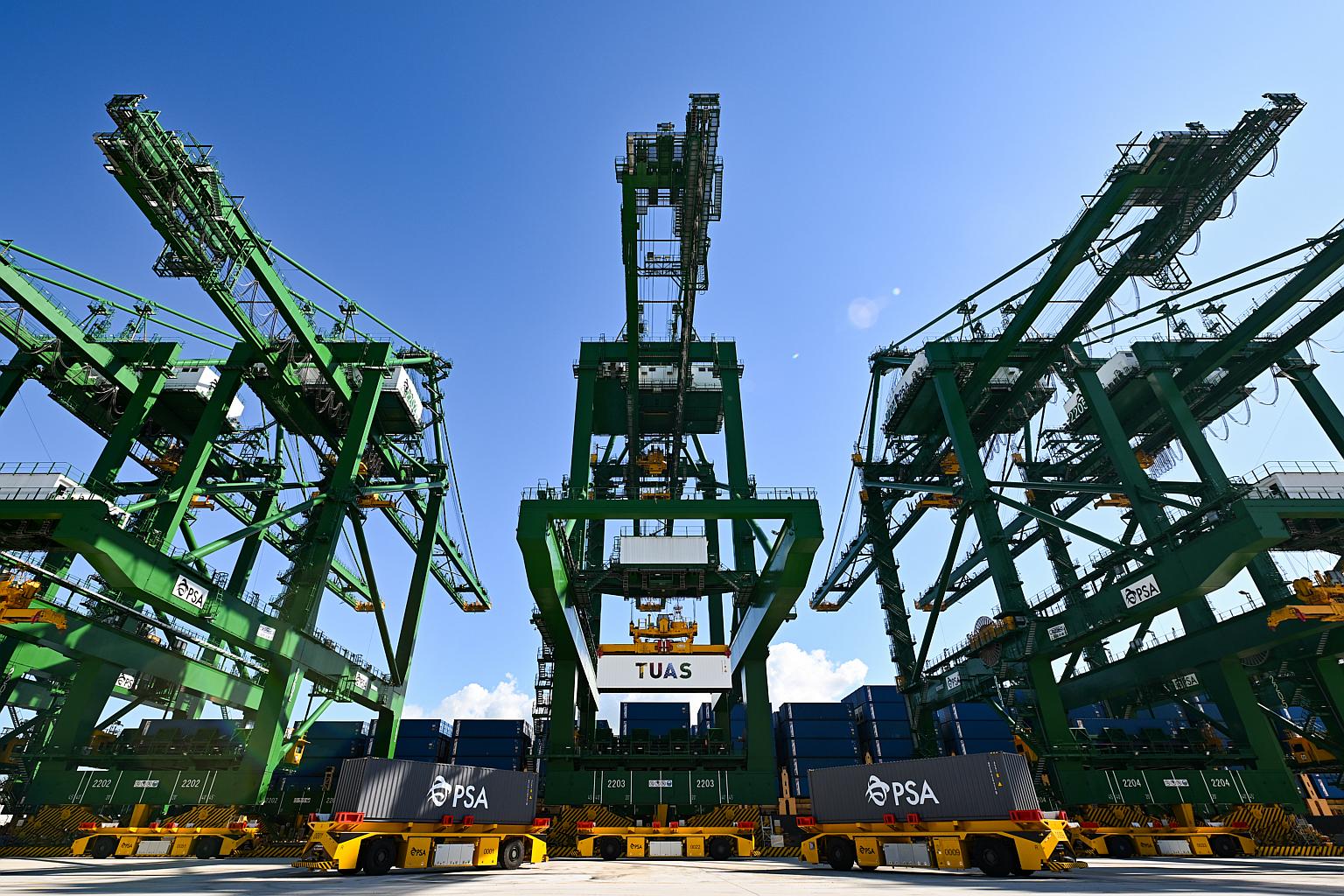
Tuas Port (Source: Straits Times)
For example, Singapore’s Tuas Port, the world’s largest fully automated port, utilises autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) for container transport, stacking, and yard management, significantly boosting efficiency and reducing reliance on manual labour.
Why Automation and Robotics Matter:
Automation and robotics are reshaping logistics, agriculture, manufacturing, and even healthcare – all vital to Singapore’s economic stability and growth. Skilled engineers who can program, troubleshoot, and optimise these systems are critically needed to sustain Singapore’s innovation edge and enhance labour productivity.
Key Skills to Build:
- Robot Operating System (ROS 2): Learn this popular open-source framework that provides a flexible environment for building modular robotic applications and enabling seamless system integration.
- Computer Vision: Develop proficiency in enabling robots to interpret and analyse visual inputs critical for navigation, inspection, and interaction.
- Machine Learning and Reinforcement Learning: Gain the expertise to train robots to adapt, learn from experience, and autonomously improve their performance in complex, dynamic environments.
Action Step:
Begin by developing a simple robotic application using accessible open-source hardware kits such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi. Experiment with programming basic autonomous behaviours and integrating sensors to gain foundational experience that will prove invaluable when working on more advanced polyfunctional systems.
Digital Trust, AI Governance & Disinformation Security
As AI technologies become increasingly integrated into critical systems, the need for governance frameworks and trust mechanisms to ensure ethical, transparent, and responsible AI use is critical.
Singapore has emerged as a global leader in this space with its Model AI Governance Framework serving as a practical and internationally recognised guide for organisations deploying AI responsibly.
Why AI Ethics Matter:
Roles specialising in AI ethics, trust and safety, regulatory compliance, and risk management are projected to be critical within future tech teams, ensuring AI systems are designed, deployed, and monitored with robust governance that earns public and stakeholder trust.
Skills to Explore:
- AI Ethics Frameworks: Mastering Singapore’s Model AI Governance Framework and understanding global guidelines such as the OECD AI Principles.
- ISO/IEC 42001 Standards: Learning about emerging ISO standards for AI management systems to ensure conformity with international best practices.
- Risk Management and Trust Design: Developing competency in identifying AI risks, creating transparent governance models, and embedding trust mechanisms into AI lifecycle management.
Action Step:
Take a short course on AI governance from local institutions such as the Singapore Computer Society or other IMDA-supported programmes.
Complement this by drafting a sample risk assessment for an AI application that interests you, focusing on fairness, transparency, and accountability risks to solidify practical understanding. Try using IMDA’s AI Verify Testing Framework as a starter.
These emerging technologies are not just shaping the future of IT but also opening up entirely new avenues for career growth. Now, we look at how you can navigate this dynamic landscape and continuously adapt your skills.
Career Roadmap & Continuous Learning
As you navigate the exciting world of emerging technologies, remember that each domain opens unique career pathways, from entry-level to specialist to strategic leadership roles. Embracing continuous learning is not just an advantage; it’s a necessity in this rapidly changing landscape.
National Support for Upskilling
Singapore supports continuous upskilling through initiatives like:
- SkillsFuture Singapore
Provides every Singaporean with credits to utilise on industry-recognised tech courses, micro-credentials, and certifications. These cover everything from foundational IT skills to advanced topics in AI and cloud computing. - TeSA (TechSkills Accelerator)
Tailored for the tech sector, offering job conversion programmes, company-led training, and career progression support. TeSA collaborates with industry leaders to ensure that what you learn aligns with the demands of employers. - Other Initiatives
As of 2025, initiatives like the Digital Skills for Life (DSL) framework and enhancements to SkillsFuture Level-Up Programme provide even more flexible, stackable credentials and hands-on apprenticeships, making “learn and earn” options more accessible for working adults while making upskilling achievable at any career stage.
Example Career Pathways by Technology Domain
| Entry-Level Role | Specialist/Intermediate | Advanced/Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Edge Developer | Edge Architect | Compute-to-Cloud Strategist |
| Junior AI Engineer | Model Tuning Specialist | AI Solutions Architect |
| IoT Technician | Smart Infrastructure Engineer | Sustainability Technology Strategist |
You can regularly access updated training and skills maps from SkillsFuture Singapore and TeSA, developed in partnership with Singapore’s leading tech employers and education institutions.
Top Certifications to Help You Stand Out
Certifications to consider:
- CompTIA Data+
- AWS Cloud Practitioner
- IBM Quantum Developer
- Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate
Your 90-Day Learning Sprint
Set yourself a concrete goal:
- Pick a micro-credential or certification via SkillsFuture Singapore, TeSA, or from global providers.
- Learn by doing: As you progress, create a personal project—perhaps a smart IoT dashboard, an AI model, or a serverless cloud app.
- Show your commitment: Share your finished project on GitHub or LinkedIn. This demonstrates initiative, real-world skills, and a drive to grow—qualities highly valued by Singaporean employers and the local tech community.
Singapore’s digital-first economy demands tech talent who are always learning. Certified specialists and strategic leaders are needed across areas like smart city development, green IT, and data-driven businesses.
By maximising the benefits of national development schemes and actively pursuing your own growth, you position yourself for ongoing opportunities and innovation.
Conclusion
Emerging technologies in IT—from generative AI and quantum computing to edge computing and green IT—are reshaping industries and creating new, exciting career opportunities.
Here in Singapore, this is further amplified by government support and a strong ecosystem for innovation that positions our nation at the very forefront of technological advancement.
Instead of spreading yourself thin, focus on building strong fundamentals, then select one technology domain to dive deep into.
Active curiosity, practical projects, and a mindset of continuous learning are your keys to staying adaptable, relevant, and highly employable in Singapore’s digital economy.
Pick a technology today, enrol in a course, and start a 90-day project to showcase your skills. Your future IT career in Singapore starts now.
Ready to Get Your IT Career Started?
To keep your skills sharp and your career future-proof, it’s essential to keep learning and adapting. @ASK Training can be your ally in this rapidly changing digital landscape!
We offer a wide selection of full and modular IT programmes, perfect for anyone looking to launch or advance their tech journey.
Some of our in-demand IT courses worth exploring:
- Emerging Technologies and Trends: Dive into the fundamentals of the cloud, automation, and current tech trends.
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Learn to defend against cyber threats, master ethical hacking, and conduct penetration testing.
- Cloud Computing: Get hands-on with virtual networks, subnets, and configure security across different cloud environments.
- IT Infrastructure and Operations: Gain strategic and technical knowledge in planning, designing, and optimising robust IT infrastructure.
Stay relevant, stay competitive and explore our courses today!
Related Courses
- Certificate in Infocomm Technology (Infrastructure and Operations)
- IT Foundations Courses
- Cloud Computing
- Cybersecurity Courses
◆◆◆


