Let’s talk honestly about where technology is heading. If you’re working in IT right now, you’ve probably noticed how quickly things are changing.
The tools we used daily just a few years ago are being replaced, and new technologies are emerging faster than ever.
The Reality of Tech Today in Singapore
- Change is constant: Remember when virtualisation was the hot topic? Now we’re talking about AI writing code and quantum computing on the horizon.
- Job requirements are evolving: That certification that helped you land your current role might not be enough for your next promotion.
- Opportunities favour the prepared: The professionals doing well aren’t necessarily the smartest; they’re the ones who keep their skills current.
Here are some local data points for professionals who invest in upskilling:
- 69% of Singaporean workers experienced better work performance after skills training (Source: The Economic Times)
- 64% credited their career growth to this training in 2024 (Source: The Economic Times)
- A 2025 survey by Indeed found that 56% are planning to upskill in AI and leadership to future-proof their careers (HRSEA Economic Times)
This guide will be your practical roadmap to:
- Identifying relevant technical and soft skills for 2025
- Taking action with clear learning pathways
Let’s explore how you can prepare for what’s next.
Understanding Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
As the nation pushes forward with its Smart Nation initiative, emerging technologies are becoming the foundation of our digital economy.
What exactly does it mean for IT professionals? Let’s break it down.
Defining Emerging Technologies in Today’s Context
When we talk about emerging technologies, we’re referring to innovations that are:
- Disrupting traditional ways of working (AI automating manual processes)
- Creating entirely new industries (Web3 and blockchain applications)
- Requiring new skill sets (cloud-native development, AI ethics)
Emerging technologies include:
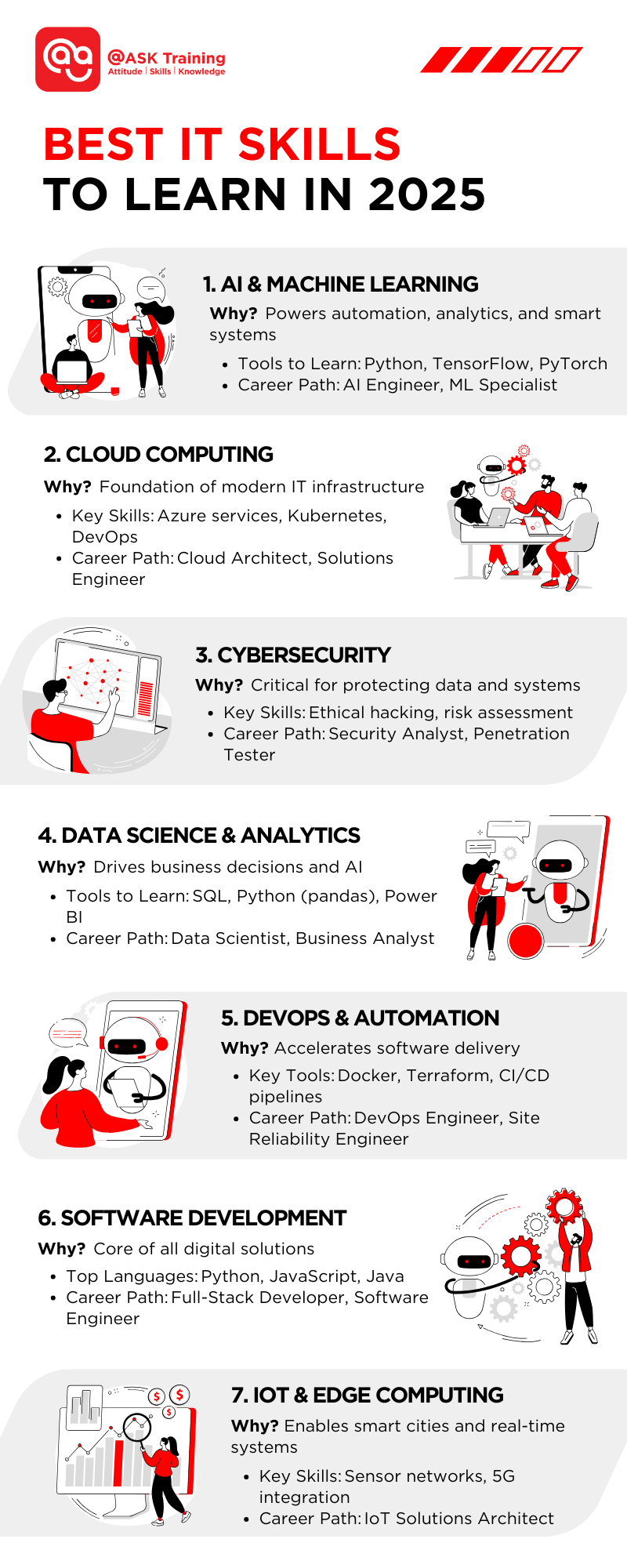
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): From chatbots to predictive analytics, AI is transforming customer service, finance, and healthcare.
- Cloud Computing: With Singapore positioning itself as a digital hub, cloud adoption is accelerating across SMEs and enterprises.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart Nation initiatives rely on IoT for everything from traffic management to energy-efficient buildings.
- Cybersecurity: As digital threats continue to grow, the demand for experts in ethical hacking, compliance, and risk management is surging.
- 5G & Edge Computing: Enabling faster, real-time data processing for industries like manufacturing and logistics.
How Tech Evolution is Reshaping Careers?
The speed of technological adoption in Singapore is creating both challenges and opportunities:
Job Market Transformations
New roles emerging:
- AI Prompt Engineers
- Cloud FinOps Specialists
- Quantum Computing Researchers
Traditional roles evolving:
- Software developers now need AI integration skills
- Network engineers must understand software-defined networking
Singapore Tech Employment Trends
This table reveals the tech employment market emerging in Singapore:
| Sector | Projected Growth 2025 | Highlights |
| Information & Communications | ~3.4% employment growth in 2024; continued modest growth expected in 2025 | Sector added ~5,900 jobs in 2024; focus on AI, cloud, cybersecurity |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | 40% increase in demand across finance, healthcare, logistics | Government aims to triple AI practitioners to 15,000 in 5 years |
| Cybersecurity | 45% growth in demand | Driven by 69.4% rise in cybercrimes; critical for fraud prevention |
| Cloud Computing | Strong demand for cloud architects and engineers | Multi-cloud expertise (AWS, Azure, GCP) highly valued |
| Advanced Manufacturing & Robotics | 25,000+ new roles projected | Part of broader tech ecosystem growth |
| Data Science / Analytics | High demand continues, especially in finance, e-commerce, healthcare | Despite some salary cooling, remains critical skill set |
| Gaming & Platform Reliability | Salary growth: Game Engineer +28%, Site Reliability Engineer +10.5% | Reflects growing demand in gaming and platform stability roles |
| Software Engineering | Modest salary growth (~3.3%) with steady hiring | Full-stack developers remain in demand |
(Sources: MOM, Randstad Singapore, Singapore Global Network, The Independent SG, Charlton Media Group)
Key Takeaway: While foundational tech roles remain stable, the most significant career opportunities lie in AI, cybersecurity, and cloud specialisations, where Singapore is making concentrated investments.
Now that we understand the landscape, let’s examine how you can develop these top IT skills, starting with AI and Machine Learning skills.
#1 Mastering Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Imagine machines that learn, adapt, and even predict. That’s the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), two of the hottest emerging technologies skills today.
Core Concepts
- AI: The broader concept of machines performing human-like tasks
- ML: A subset of AI focused on systems learning from data without explicit programming
- Key Difference: AI is the umbrella term (like “vehicles”), while ML is a specific approach (like “electric cars”)
Essential ML Framework: Industry Standard Tools
| ML Framework / Tool | Usage in Tech Ecosystem | Notes |
| TensorFlow | Deep learning, neural networks, large AI models | Used in AI research and production |
| PyTorch | NLP, computer vision, research & prototyping | Favoured for flexibility and innovation |
| Scikit-learn | Classical ML algorithms for finance, healthcare, analytics | Widely used for prototyping and deployment |
| Keras | High-level deep learning API | Supports rapid experimentation |
Tip: Most AI roles expect TensorFlow or PyTorch proficiency
Example of Building Your ML Model: A Simple Guide
Let’s build a simple Machine Learning (ML) model to classify emails as “spam” or “not spam.”
1. Get Labelled Data
Collect many emails, each clearly marked as either “spam” or “not spam.” This is your training material.
2. Prepare the Data
- Clean: Tidy up the emails (remove junk).
- Convert to Numbers: Turn the email text into numbers that the computer can understand (e.g., counting specific words).
- Split: Divide your data into two sets: one for the computer to learn from, and a smaller one to test its learning.
3. Choose an Algorithm
Pick a suitable ML method. For “spam vs. not spam,” a good start is Logistic Regression (a common way to sort into two groups) or a Decision Tree (like a flowchart).
4. Train the Model
The computer “learns” by looking at your “learning” emails and their labels. It finds patterns to tell spam from non-spam.
5. Evaluate Performance
Use the “test” emails (which the model hasn’t seen) to check how accurately it classifies them. This tells you how well your model will perform on new, real-world emails.
6. Make Predictions
Once trained and evaluated, your model can now predict if any new, incoming email is “spam” or “not spam.”
Learning Pathways
1. Foundation First
Begin with Google’s Machine Learning Crash Course. This is a free, hands-on online course that gets you coding quickly using TensorFlow (a popular tool for ML). It’s great for learning by doing.
2. Code in Python
Python is the go-to language for ML. Learn its basics and then explore libraries like Scikit-learn, which makes building models easier. DataCamp offers great interactive courses for this.
3. Hands-On Learning
Theory is good, but applying it is better. Work on small projects or try simple challenges on platforms like Kaggle to build real skills.
4. Focus on Understanding
Don’t just copy code. Try to grasp why each step is taken and what it achieves.
5. Stay Curious & Connected
The ML field is always evolving. Join online communities to ask questions, share knowledge, and keep learning.
Now that we’ve covered AI/ML fundamentals, let’s examine another high-growth area: Cloud Computing.
#2 Leveraging Cloud Computing for Scalable Solutions
Cloud computing isn’t just a tech buzzword; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses build and deliver flexible, scalable solutions.
Understanding Cloud Computing
At its core, cloud computing offers three main service models:
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- What it is: Virtualised computing resources over the internet (servers, storage, networking)
- When to use: When you need full control over OS and middleware
- Example: AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- What it is: Development environment with built-in tools and services
- When to use: When you want to focus on coding without managing infrastructure
- Example: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, Google App Engine
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- What it is: Ready-to-use applications delivered over the web
- When to use: When you need business applications without development
- Example: Salesforce, Slack, Google Workspace
Overview of Major Cloud Platforms
A few major players dominate the cloud landscape, each offering a vast array of services:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): The most mature and widely adopted cloud platform, offering a comprehensive suite of services.
- Microsoft Azure: A rapidly growing platform, particularly popular among enterprises already invested in Microsoft technologies.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Known for its strengths in data analytics, machine learning, and containerization, leveraging Google’s global infrastructure.
Example
A fantastic example use case that showcases the power of cloud computing is deploying a microservices application.
Instead of building one giant application, microservices break it down into smaller, independent services that communicate with each other.
The cloud provides the perfect environment to host these services, allowing each to scale independently based on demand, leading to more resilient and agile applications.
Learning Pathways
To truly validate your expertise and boost your cloud computing skills, consider pursuing certifications.
The Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert is an excellent starting point and highly recognised in the industry. Steps to achieve it typically involve:
1. Learning the Fundamentals:
Understand core Azure services such as Virtual Machines, Storage, Virtual Networks, and Azure SQL Database to build your foundational knowledge.
2. Hands-On Practice:
Build small projects on Azure by deploying resources using the Azure portal, CLI, and ARM templates to gain practical experience.
3. Study Exam Content:
Review the AZ-305 exam objectives, focusing on designing secure, scalable, and cost-effective cloud solutions with best practices in governance and architecture.
4. Practice Tests:
Take official or reputable practice exams to assess your readiness and identify areas needing improvement. Use results to guide your final revision before sitting for the exam.
With cloud infrastructure established, security becomes crucial. Next, let’s explore cybersecurity.
#3 Stregthening Cybersecurity Foundations
In an increasingly interconnected world, cybersecurity isn’t just an IT department’s concern; it’s everyone’s responsibility.
Protecting digital assets from theft, damage, or unauthorised access is paramount. Cybersecurity encompasses several critical domains:
1. Network Security
- Protects data in transit (firewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection)
- Example: Configuring AWS Security Groups to restrict unauthorised access
2. Application Security
- Secures software from vulnerabilities (OWASP Top 10 risks)
- Example: Implementing input validation in web forms
3. Endpoint Security
- Safeguards devices (antivirus, encryption, mobile device management)
- Example: Enforcing full-disk encryption on corporate laptops
Risk Assessment & Compliance
Risk assessment involves identifying, analysing, and evaluating potential cybersecurity risks to an organisation’s assets.
This includes:
- Conducting regular audits using frameworks like ISO 27001
- Understanding regional regulations: GDPR (EU), PDPA (Singapore)
Example: Mitigating A Phishing Attack Scenario
- Detection: Employee reports a suspicious government-themed email
- Containment: Isolate affected devices, revoke compromised credentials
- Remediation: Implement MFA, conduct staff awareness training
Learning Pathways
To solidify your expertise in this crucial field, pursue highly respected certifications:
- CompTIA Security+: An entry-level certification that covers the essential principles for network security and risk management.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): A well-known certification that validates your ability to think like a hacker by understanding vulnerabilities, attack vectors, and ethical hacking techniques to better defend systems.
- CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional): A more advanced and globally recognised certification for experienced security practitioners.
These cybersecurity skills are consistently in-demand tech skills for 2025. As we solidify our security posture, this foundation becomes even more crucial when handling sensitive data, which leads us naturally to the following emerging skills.
#4 Excelling in Data Science and Analytics
Transform raw data into powerful, actionable insights that drive strategic decisions. Master the entire data science lifecycle:
- Collection: Diligently gather diverse datasets from various sources.
- Analysis: Perform in-depth analysis to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Visualisation: Create compelling visualisations that clearly communicate findings and tell a story to stakeholders.
Key Tools Commonly Used
Arm yourself with the essential tools for data mastery:
- Python (pandas): With powerful libraries like pandas for data manipulation.
- SQL: For efficiently managing and querying large databases.
- Tableau: For creating interactive and insightful dashboards.
Example: Conducting Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) on a Sample Dataset
1. Begin by importing your dataset into pandas, typically from a CSV file or similar data source.
2. Use fundamental pandas methods to examine your data:
- .head() displays the initial rows
- .info() reveals the data structure
- .describe() provides statistical summaries
3. Perform data cleaning by addressing:
- Missing values through imputation or removal
- Outliers that may skew your analysis
4. Create visual representations using libraries like matplotlib or seaborn to:
- Plot histograms for distribution patterns
- Generate boxplots to identify outliers
- Develop scatter plots to examine relationships
Through this process, you’ll uncover meaningful patterns, anomalies, and insights that can guide subsequent modelling decisions or business recommendations. For further learning, try this tutorial by Microsoft.
Learning Pathways
To accelerate your journey in data science skills, explore suggested learning pathways through:
Online Learning Platforms (MOOCs):
- Coursera, edX, and DataCamp, offer structured courses that cover essential data science topics.
- These include Python coding, database querying with SQL, and creating compelling data visualisations – all available through flexible online study.
Practical Data Challenges (Kaggle):
- The Kaggle platform offers valuable hands-on experience by hosting competitions with authentic datasets.
- You can develop crucial abilities in data preparation, analytical techniques, and visual presentation while solving actual business problems.
Working with data efficiently requires streamlined processes. That’s where DevOps comes into play as the next IT skill.
#5 Implementing DevOps and Automation Practices
DevOps brings software developers and IT operations teams together. Instead of working separately, they actively collaborate to build, test, and release software faster and more reliably.
This teamwork helps companies deliver new features and fixes quickly while keeping systems stable.
A key part of DevOps is CI/CD, which stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (or Deployment):
- Continuous Integration (CI): Developers frequently merge their code changes into a shared project. Automated tools then build and test the code to catch errors early.
- Continuous Delivery (CD): After testing, the system automatically prepares the software for release. In continuous deployment, the system even automatically sends the software to users without manual steps.
Together, CI/CD pipelines automate the process of building, testing, and releasing software, reducing mistakes and speeding up delivery.
Essential DevOps Tools
Here are some essential DevOps tools skills:
- Docker: You package applications and their dependencies into containers, so they run the same everywhere.
- Kubernetes: You manage and scale many containers automatically, ensuring apps stay available.
- Terraform: You write code to create and manage cloud infrastructure (servers, networks) automatically and consistently.
- PowerShell: You use this scripting language mainly to automate tasks and manage Windows systems.
Example: Creating an Automated Deployment Pipeline
Imagine you want to release a new app feature quickly and safely. Here’s how a CI/CD pipeline helps:
- Developers write and commit code to a shared repository (like Git).
- The pipeline automatically builds the app and runs tests to check for bugs.
- If tests pass, the system packages the app into a Docker container.
- The system deploys the container to a Kubernetes cluster, which runs and manages the app.
- Monitoring tools keep an eye on the app’s health and alert teams if issues arise.
This automation means new features reach users faster with fewer errors.
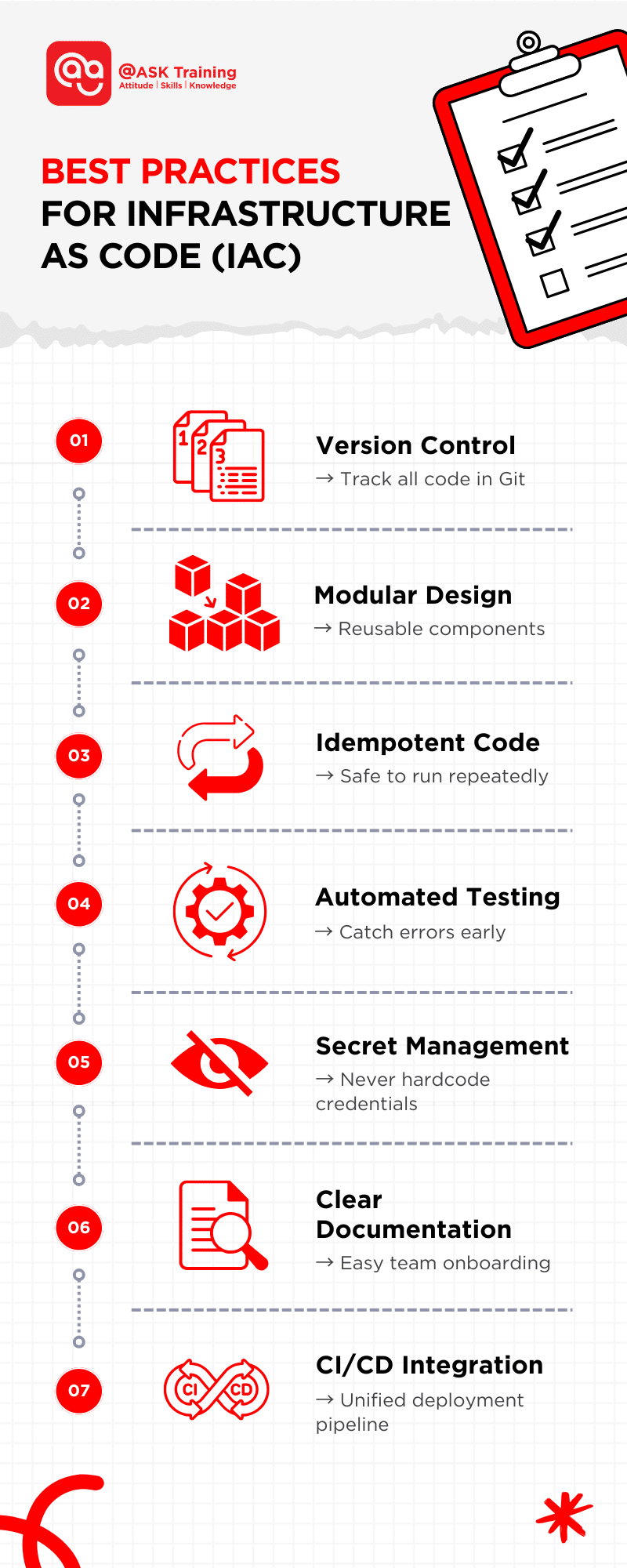
Best Practices for Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Use Version Control: Always keep all infrastructure code in systems like Git to track changes.
- Write Modular Code: Break configurations into reusable pieces for easier updates.
- Ensure Idempotency: Design your code so running it multiple times causes no problems or unexpected changes.
- Automate Testing: Actively test your infrastructure code to catch errors early.
- Secure Secrets: Never hardcode passwords or keys; use secure storage solutions.
- Document Clearly: Always make sure your code and processes are easy for your team to understand.
- Integrate with CI/CD: Automate infrastructure changes alongside application code for smoother deployments.
By learning DevOps culture, mastering these tools, and following best practices, you empower teams to deliver software faster, more reliably, and with less manual effort.
Automation is powerful, but it all starts with writing quality code. Let’s examine core programming skills.
#6 Developing Core Programming and Development Skills
Developing strong core programming skills empowers you to create the very tools and applications that drive innovation. Forge the foundational abilities to build, customise, and innovate, creating the digital solutions of tomorrow.
Top Programming Languages to Learn in 2025
These are some common programming languages for tech:
- Python: This is the most popular language today, loved for its simplicity and versatility. You widely use it in data science, AI, web development, and automation. Python is excellent for beginners and remains highly relevant for future tech jobs.
- Java: You choose Java for building large-scale applications, especially in enterprises. It runs on many devices and provides strong stability and scalability.
- JavaScript: This essential language powers web development, creating interactive websites and web apps. You also use it on the server side with Node.js.
Popular Frameworks to Know
Beyond the languages, leverage popular frameworks to accelerate your development efforts:
- React: You use this JavaScript library to build engaging user interfaces, especially for single-page web applications.
- Spring Boot: This Java framework simplifies building backend applications and REST APIs, letting you focus on logic.
- js: You use this JavaScript runtime to build fast, scalable server-side applications, extending JavaScript’s reach.
Example: Building a REST API with Node.js
A REST API lets various software communicate over the internet. Using Node.js, you can quickly create a simple API by:
- Setting up a Node.js project.
- Using the Express framework to define routes (URLs) that respond to requests.
- Handling data input and output in JSON format.
- Connecting to a database to store and retrieve data.
This hands-on project helps you understand how web services work and provides an excellent way to practice backend development.
Learning Pathways
The most effective way to solidify your development skills is through project-based learning. This approach helps you truly master programming:
- Build Real Projects: Learning by doing is the best way to master programming. Start with small projects like a to-do list app, a blog, or a simple game.
- Use Online Platforms: Websites like GitHub, Codecademy, and freeCodeCamp offer guided projects and community support to keep you on track.
- Contribute to Open Source: Join open-source projects to collaborate with others and see how real-world software is built, gaining invaluable experience.
- Practice Regularly: Coding daily, even for short periods, helps reinforce concepts and significantly improves your problem-solving skills.
Technical skills alone aren’t enough; they need to be complemented with strong interpersonal abilities, which brings us to the next section.
#7 Cultivating Essential Soft Skills for Tech Professionals
Technical skills open doors, but essential soft skills for tech professionals drive excellence, leadership, and impactful contributions.
These attributes differentiate top performers and build cohesive, productive teams. In tech, strong technical skills are vital, yet communication, teamwork, and problem-solving prove equally crucial.
Use these skills to collaborate effectively, understand user needs, and solve challenges directly.
Communication and Teamwork: Leading Effective Sprint Retrospectives
Lead sprint retrospectives to improve team performance. To make these meetings effective:
- Encourage open, honest communication.
- Listen carefully to all feedback, without interruption, for full understanding.
- Focus on solutions and learning, not blame, fostering a positive environment.
- Collaborate to create actionable plans for improvement.
This process builds trust and teamwork, directly smoothing project execution.
Tips to Improve Soft Skills
- Active Listening: Practice deep attention when others speak. In a “Paraphrase Challenge,” one talks, others listen, then repeat in their own words. This improves understanding and reduces miscommunication.
- Empathy in User-Centred Design: See situations from the user’s perspective. Understand their feelings, needs, and challenges. This empathy directly leads to better product designs and happier users.
Recommended Resources
Books:
- “Crucial Conversations”: Learn how to communicate effectively in high-stakes situations.
- “The Five Dysfunctions of a Team”: Understand teamwork dynamics and how to build strong teams.
Workshops and Online Courses:
- Look for workshops on active listening and emotional intelligence.
- Platforms like LinkedIn Learning offer courses on communication and teamwork skills.
By developing these soft skills alongside your technical abilities, you’ll become a well-rounded tech professional who can collaborate effectively and lead projects to success.
Wrapping Up
The future of technology is here, and it’s evolving faster than ever. From AI and cloud computing to cybersecurity and DevOps, the skills that will define the next generation of IT professionals are clear.
But knowledge alone isn’t enough; action is what separates those who adapt from those who get left behind.
Key Takeaways from This Guide
- Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and 5G are reshaping industries—staying updated is non-negotiable.
- High-demand skills (cloud architecture, cybersecurity, data science) offer the best career growth opportunities.
- DevOps and automation streamline software delivery, making them critical for efficiency.
- Programming fundamentals (Python, JavaScript, Java) remain the backbone of tech innovation.
- Soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, amplify your technical expertise.
Your Next Steps
- Pick One Skill to Master First: Start with what excites you most (e.g., AI basics, cloud certifications, or Python programming).
- Leverage Free Resources: Platforms like Coursera, Kaggle, and GitHub offer hands-on learning.
- Build Real Projects: Apply what you learn through small, practical applications.
- Join a Tech Community: Engage with peers for support, mentorship, and collaboration.
The Bottom Line
The tech landscape rewards those who learn, adapt, and execute. Whether you’re an early-career professional or a seasoned expert, 2025 is your year to upskill, stand out, and lead.
Ready to Start Your Tech Career?
Your journey to becoming an indispensable IT professional starts now with @ASK Training!
We offer various IT certifications, full-time and modular programmes that are designed to equip you with these emerging practical skills to excel!
Here are a few recommended upskilling pathways for you:
- Certificate in Infocomm Technology (Infrastructure and Operations)
- IT Foundations Courses
- Cybersecurity Courses
- Cloud Computing
Enrol with us and start your tech career today!
Related Courses
- Certificate in Infocomm Technology (Infrastructure and Operations)
- IT Foundations Courses
- Cloud Computing
- Cybersecurity Courses
◆◆◆